Curie Temperature Predictions
Curie temperature is one of the important properties for permanent magnetic materials. The Curie temperature (Tc) is a critical temperature, above which certain materials lose their permanent magnetic properties. Considering the high-temperature range of practical usage of traction motors of cars up to 450 K, it has been in high demand to find a way to supplement the high-temperature performance of Nd-Fe-B magnets or to design a new champion magnet desirably with higher Curie temperatures with a good structure stability [2020Mat].
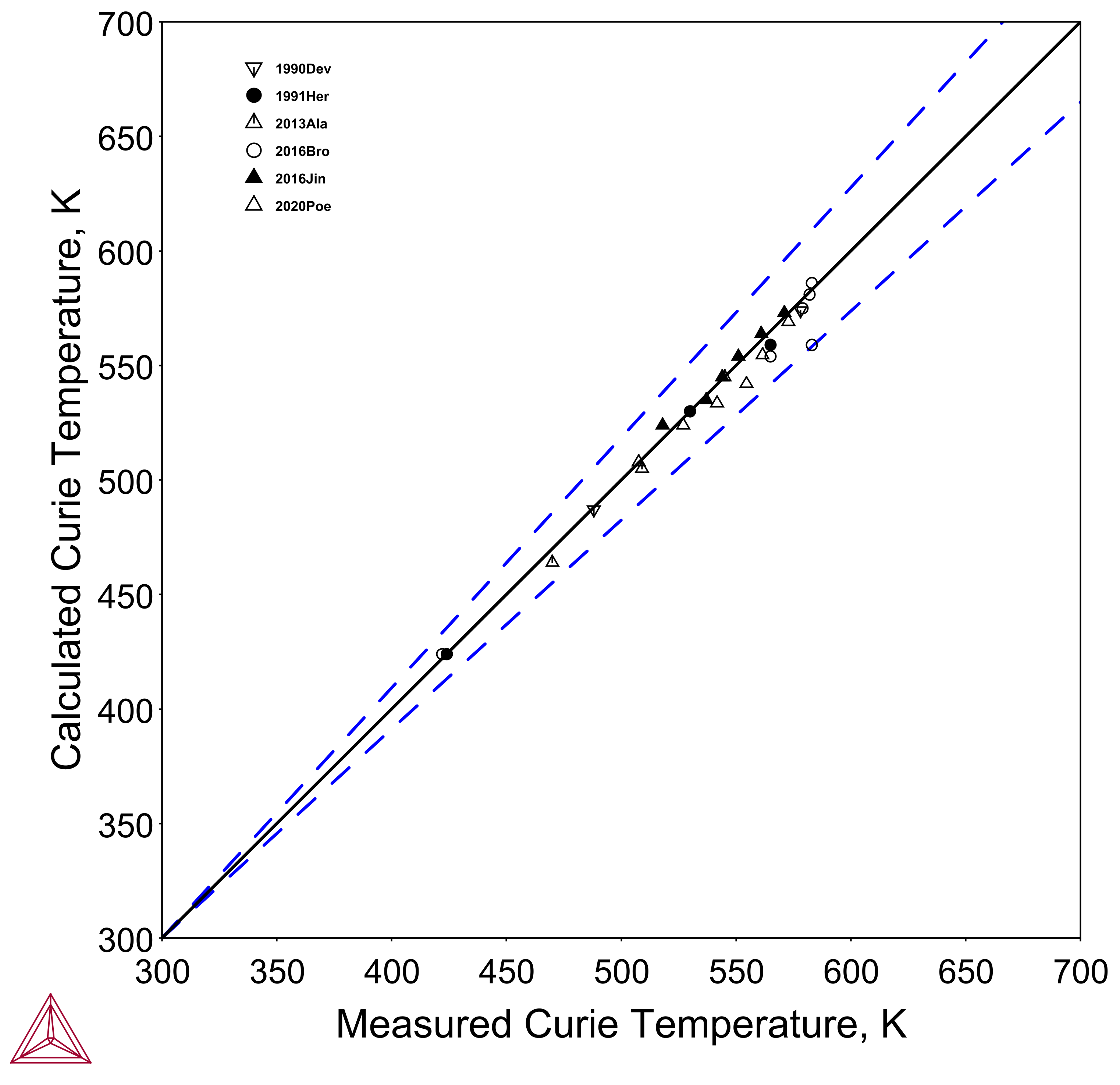
The TCS Permanent Magnetic Materials Database (TCPMAG) includes magnetic parameters for phases with magnetic properties. Thus, it can be used to predict the curie temperatures of a magnetic phase as a function of the chemical composition of typical industrial alloys. The figure below shows the comparison of calculated and measured curie temperature for (Ce,La,Nd,Pr)2Fe14B (T1) phase. In all cases, the differences are less than 5%.
Reference
[2020Mat] M. Matsumoto, H. Akai, Calculating Curie temperatures for rare-earth permanent magnets: Ab initio inspection of localized magnetic moments in d -electron ferromagnetism. Phys. Rev. B. 101, 144402 (2020).