About the Strain-Age Cracking Property Model
The Strain-Age Cracking - Ni Property Model, available with the Property Model Calculator and the Nickel Model Library, is used in applications related to welding or additively manufactured components, where there are interface strains between γ' (gamma prime) and the matrix.
To run calculations with the Nickel Models requires a valid maintenance license plus licenses for both the TCNI (version 11 and newer) and MOBNI (version 5 and newer) databases. For some Property Models, additional recommendations for the database version to use is indicated in its description. Also see our website to learn more about the Nickel Model Library.
For best results with this Property Model and the features it uses, it is recommended to use TCNI version 12 and newer.
Strain-age cracking (SAC) may occur in welded or additively manufactured components due to interface strains between γ' (gamma prime) and the matrix. The interface strain may be quantified as a misfit parameter, i.e.
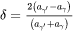
where  is the lattice parameter of each respective phase (γ matrix or γ') in conjunction with residual thermal stresses from welding or additive manufacturing. Strain-age cracking may occur at negative values of the misfit parameter in combination with thermal stresses and the risk for cracking is also related to the γ' volume fraction.
is the lattice parameter of each respective phase (γ matrix or γ') in conjunction with residual thermal stresses from welding or additive manufacturing. Strain-age cracking may occur at negative values of the misfit parameter in combination with thermal stresses and the risk for cracking is also related to the γ' volume fraction.
Misfit strain naturally varies with temperature (thermal expansion) and phase composition (molar volume depends on composition and temperature) and therefore an accurate assessment of the strain-age cracking risk must account for these variables. When defining this Model on the Configuration window, this is managed using either a Single temperature or Temperature interval mode.
Single Temperature Mode
When using the Single temperature mode, the model evaluates the misfit parameter at the temperature and composition specified. By stepping in temperature or composition (or both), it is possible to get an idea of how the misfit varies. Misfit values calculated using this mode can be compared with experiment but it is necessary to remember that comparisons are only valid if experimental data are taken from fully equilibrated alloys.
Temperature Interval Mode
The Temperature interval mode circumvents the issue of having to compare with fully equilibrated alloys. It provides a single parameter to describe the tendency for strain-age cracking. When using this mode, the Model searches for a temperature interval, between the lower limit (this is the Temperature set under Condition Definitions) and the upper limit (by default the calculated γ' solvus, which can also be changed by using the Set maximum temperature checkbox), where the misfit parameter becomes negative.
The misfit value, and the γ' volume fraction is then integrated over the interval where the misfit is negative and the risk value for strain-age cracking is thereafter calculated.
Values of the SAC risk factor close to or below 0 indicate low or no risk for strain-age cracking. Positive values indicate risk for cracking and the more positive the value, the higher the risk. The risk factor, as defined here, also incorporates all thermodynamically related factors for strain-age cracking and makes it possible to differentiate the SAC risk for various alloys using a single number for any given temperature interval.
The input parameters are entered on the Configuration window for the Property Model Calculator. There are also settings on the Plot Renderer where you can choose from the available and relevant axis variables.
See Strain-Age Cracking Property Model Settings for details.
For an example, see PM_Ni_04: Strain Age Cracking (SAC).
[2024Kap] B. Kaplan, A comprehensive model for quantitatively predicting the comparative Strain-Age Cracking risk in welded or additively manufactured Ni-base superalloys. In press, Mater. Today Commun., 40, 109408 (2024).