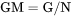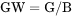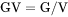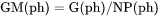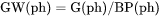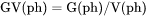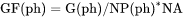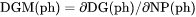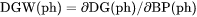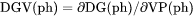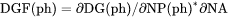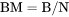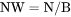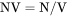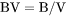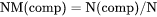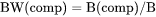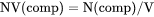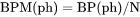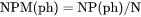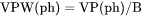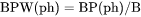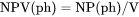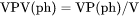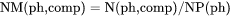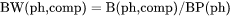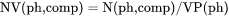Suffixes
Suffixes may be appended to all extensive variables and to some intensive variables. Some suffixes can be used to enter the value of variables in normalized form. These are referred to as normalizing suffixes. If the variable that you create with a normalizing suffix is based on a state variable that can be set as a condition in POLY, then the normalized variable can also be set as a condition in POLY.
The normalizing suffixes are M (per mole), W (per mass in gram), V (per volume in m3) and F (per mole formula unit). There is also a reference state suffix R, which you can use if you want the value of a thermodynamic variable to be calculated with respect to a reference state that have previously set.
Normalizing Suffixes
When variables that express system and phase quantities are normalized, the following general rules are used:
- System quantities are normalized by the total system size (in terms of N, B or V).
- Phase quantities are normalized by the phase amount [in terms of NP(ph), BP(ph) or VP(ph)].
The normalized quantities of G(ph), A(ph), U(ph), H(ph), S(ph) and V(ph) are calculated according to the thermodynamic model used for the phase (e.g. GM(ph), AM(ph), UM(ph), HM(ph), SM(ph) and VM(ph)). These quantities are calculated using the first derivatives of the Gibbs energy expressed for the phase with respect to the current composition of the system.
The tables describe the normalizing suffixes for the different state variables.
| Suffix | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
M (per mole) |
Total system size in terms of N. |
GM is the Gibbs energy per mole of the system (J/mol).
|
|
W (per mass in gram) |
The total system size in terms of B. |
GW is the Gibbs energy per mass of the system (J/g).
|
|
V (per volume in m3) |
The total system size in terms of V. VV does not have to be evaluated. |
GV is the Gibbs energy per volume of the system (J/m3).
|
| Suffix | Example |
|---|---|
|
M (per mole) |
For example, GM(ph) is Gibbs energy of the phase per mole of the phase (J/mol).
|
|
W (per mass in gram) |
For example, GW(ph) is Gibbs energy of the phase per mass of the phase (J/mol).
|
|
V (per volume in m3) |
For example, GV(ph) is Gibbs energy of the phase per volume of the phase (J/mol).
|
|
F (per mole formula unit) |
For example, GF(ph) is the Gibbs energy of the phase per formula unit of the phase (J/mol).
|
| Suffix | Description | Example(s) |
|---|---|---|
|
M (per mole) |
Theoretically, the first derivative of the variable with regard to the phase amount in terms of NP(ph). Since DG(ph) is not directly calculated, the second derivative of the Gibbs energy expressed for the phase in question with respect to the current compositions in the equilibrium state of the system is calculated instead. DGM(ph) cannot not be set as a condition since it is only calculated under a certain type of equilibrium state. |
DGM(ph) is driving force for precipitation of the phase per mole of components.
|
|
W (per mass in gram) |
Theoretically, the first derivative of the variable with regard to the phase amount in terms of BP(ph). Since DG(ph) is not directly calculated, the second derivative of the Gibbs energy expressed for the phase in question with respect to the current compositions in the equilibrium state of the system is calculated instead. DGW(ph) cannot not be set as a condition since it is only calculated under a certain type of equilibrium state. |
DGW(ph) is driving force for precipitation of the phase per mass of components.
|
|
V (per volume in m3) |
Theoretically, the first derivative of the variable with regard to the phase amount in terms of VP(ph). Since DG(ph) is not directly calculated, the second derivative of the Gibbs energy expressed for the phase in question with respect to the current compositions in the equilibrium state of the system is calculated instead. DGV(ph) cannot not be set as a condition since it is only calculated under a certain type of equilibrium state. |
DGV(ph) is driving force for precipitation of the phase per volume of components.
|
|
F (per mole formula unit) |
Theoretically, the first derivative of the variable with regard to the phase amount in terms of NP(ph) and NA (NA is the total atomic number in the phase formula). Since DG(ph) is not directly calculated, the second derivative of the Gibbs energy expressed for the phase in question with respect to the current compositions in the equilibrium state of the system is calculated instead. DGF(ph) cannot not be set as a condition since it is only calculated under a certain type of equilibrium state. |
DGF(ph) is driving force for precipitation of the phase per formula unit of components.
|
| Suffix | Description | Example(s) |
|---|---|---|
|
M (per mole) |
The total system size in terms of N. NM does not have to be evaluated. BM cannot be set as a condition. |
BM is mass (gram) of components per mole of the system (g/mol).
|
|
W (per mass in gram) |
The total system size in terms of B. BW does not have to be evaluated. NW cannot be set as a condition. |
NW is mole number of components per mass of the system (mol/g).
|
|
V (per volume in m3) |
The total system size in terms of V. BV is the density of the entire system. |
NV is mole number of components per volume of the system (mol/m3).
BV is the density of the entire system (g/m3).
|
| Suffix | Description | Example(s) |
|---|---|---|
|
M (per mole) |
The total system size in terms of N. BM(comp) cannot be set as a condition. |
NM(comp) is the mole of a component per mole of the system (i.e. mole fraction, which also is expressed as X(comp)).
|
|
W (per mass in gram) |
The total system size in terms of B. NW(comp) cannot be set as a condition. |
BW(comp) is mass (gram) of a component per mass of the system (i.e. mass fraction, which also is expressed as W(comp)).
|
|
V (per volume in m3) |
The total system size in terms of V. |
NV(comp) is mole number of a component per volume of the system (mol/m3).
|
| Suffix | Description | Example(s) |
|---|---|---|
|
M (per mole) |
BPM(ph) and VPM(ph): The phase amount in terms of NP(ph). NPM(ph): The total system size in terms of N. |
BPM(ph) is mass (gram) of a phase per moles of the system (g/mol).
NPM(ph) is number of moles of a phase per moles of the system (mole fraction).
|
|
W (per mass in gram) |
NPW(ph) and VPW(ph): The phase amount in terms of BP(ph). BPW(ph):The total system size in terms of B. |
VPW(ph) is volume (m3) of a phase per mass of the system (m3/g)
BPW(ph) is mass (gram) of a phase per mass of the system (mass fraction)
|
|
V (per volume in m3) |
NPV(ph) and BPV(ph): The phase amount in terms of VP(ph). VPV(ph): The total system size in terms of V. |
NPV(ph) is number of moles of a phase per volume of the system (mol/m3).
VPV(ph) is volume (m3) of a phase per volume of the system (volume fraction).
|
| Suffix | Description | Example(s) |
|---|---|---|
|
M (per mole) |
The phase amount in terms of NP(ph) of the phase. |
NM(ph,comp) is number of moles of a component per mole of a phase (i.e. mole fraction of a component in a phase, which is equivalent to X(ph, comp)).
|
|
W (per mass in gram) |
The phase amount in terms of BP(ph) of the phase. |
BW(ph,comp) is mass (gram) of a component per mass of a phase (i.e. mass fraction of a component in a phase, which is equivalent to W(ph,comp)).
|
|
V (per volume in m3) |
The phase amount in terms of VP(ph) of the phase. |
NV(ph,comp) is mole number of a component per volume of a phase (mol/m3).
|
You can use the reference state suffix R for some thermodynamic variables to calculate their value with respect to a reference state that you have previously set for a system component with the SET_REFERENCE_STATE command in POLY (or in response-driven modules such as the POURBAIX module). The value of energy-related variables that are used with the R suffix depends on the reference states of all the components in the defined system.
It is possible to use an R suffix on all compositional extensive state variables as well, but the value of the state variable is always the same, with or without the suffix.
If the reference state for a system component is the default reference state (the stable reference state (SER) which is defined in a Thermo‑Calc database), then MUR(comp)= MU(comp), ACR(comp)= AC(comp) and LNACR(comp)= LNAC(comp).
In the case of some thermodynamic variables, you can also use the R suffix to express chemical potentials and activities of species relative to some single-substitutional-lattice solution phases (such as aqueous solution, gaseous mixture, metallic liquid solution, slag mixture or MO solid solution). These state variables are MU(sp,ph), MUR(sp,ph), AC(sp,ph), ACR(sp,ph), LNAC(sp,ph) and LNACR(sp,ph).
The reference states and standard states of various solution species are pre-defined for some solution phases in some databases. For all solution species in any solution model in any database, it is always the case that MUR(sp,ph)= MU(sp,ph), ACR(sp,ph)= AC(sp,ph) and LNACR(sp,ph)= LNAC(sp,ph).