Al-Fe-Si
Al-Fe-Si is a core system, as Fe and Si exist in all aluminum alloys either as a common alloying element or an inevitable impurity. The two Al-Fe-Si compounds, τ5: α-Al8Fe2Si and τ6: β-Al9Fe2Si2, are frequently observed in aluminum alloys. Additionally, τ4may form in high-Si aluminum alloys.
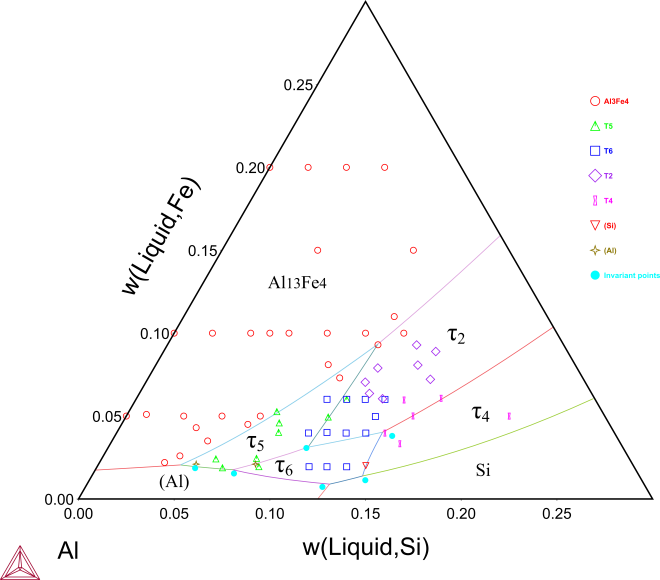
Figure 1: Calculated Al-Fe-Si liquidus projection (τ5: α-AlFeSi; τ6: β-AlFeSi), (a) in the Al-rich corner. The invariant points are from [2004Pon; 2004Bos]. The remaining data are from [1940Tak; 1967Mun; 1988Zak].
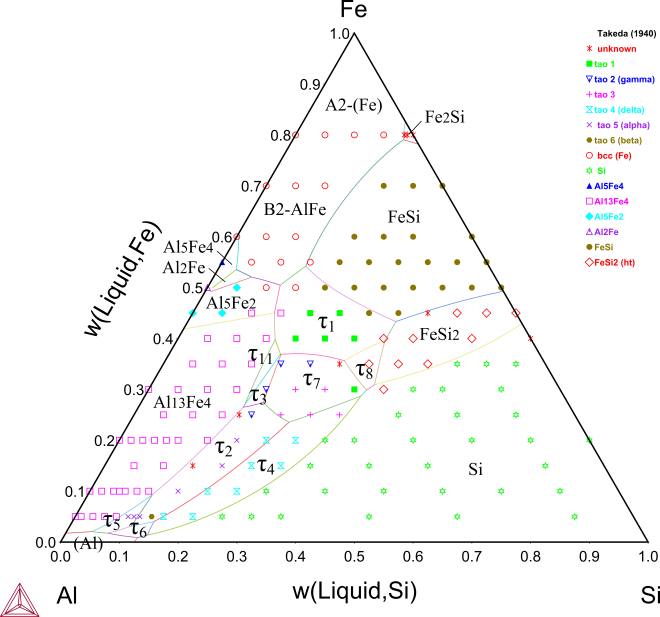
Figure 2: Continuing from Figure 1 this is over the entire compositional range, with the data from [1940Tak].
References
[1940Tak] S. Takeda, K. Mutuzaki, The equilibrium diagram of the Fe–Al–Si system. Tetsu-to-Hagane. 26, 335–361 (1940).
[1967Mun] D. Munson, A Clarification of the Phases Occurring in Aluminium-Rich Aluminium-Iron-Silicon Alloys, with Particular Reference to the Ternary Phase α-AlFeSi. J. Inst. Met. 95, 217–219 (1967).
[1988Zak] A. M. Zakharov, I. T. Gulman, A. A. Arnold, Y. A. Matsenko, Phase diagram of the Aluminium-Silicon-Iron system in the concentration range of 10-14% Si and 0-3% Fe. Russ. Metall. 3, 177–180 (1988).
[2004Bos] F. Bosselet, S. Pontevichi, M. Sacerdote-Peronnet, J. C. Viala, Experimental measurement of the Al-Fe-Si isothermal section at 1000 K. J. Phys. IV. 122, 41–46 (2004).
[2004Pon] S. Pontevichi, F. Bosselet, F. Barbeau, M. Peronnet, J. C. Viala, Solid-liquid phase equilibria in the Al-Fe-Si system at 727 °C. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 25, 528–537 (2004).