Boundary Conditions
Boundary conditions are conditions that define how matter behaves at the boundaries of your system. By default, matter is not allowed to cross the system boundaries.
You can change the setting for both the lower boundary (left side/centre) and the upper boundary (right side/surface) of the system.
Examples D_06 and D_07 use boundary conditions, as described in Diffusion Module (DICTRA) Graphical Mode Examples Collection .
The boundary condition settings are done on the Diffusion Calculator. The following describes the options available for the Left boundary and Right boundary conditions.
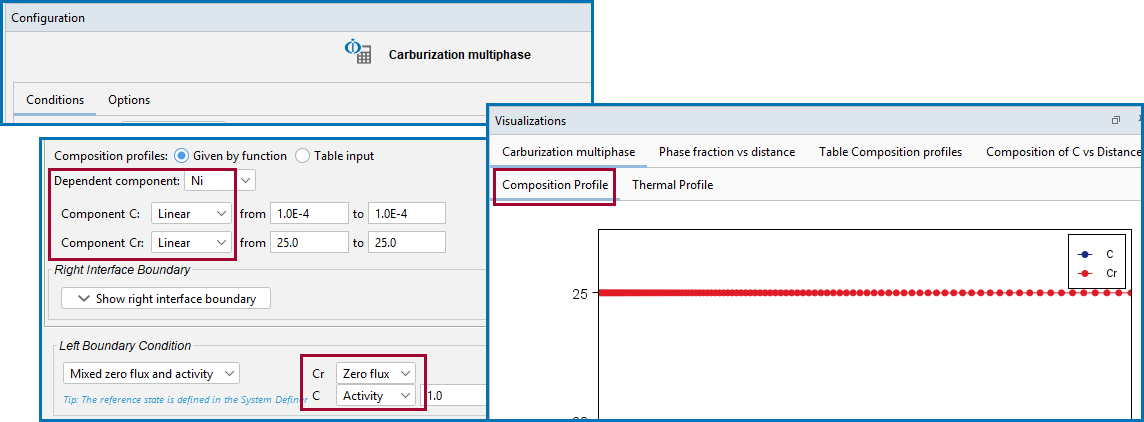
By default it is a Closed system. Choose Mixed zero flux and activity or Composition if the system is not closed. Corresponds to a fix flux value, which is set to zero at all times. This is the default boundary condition.
Allows you to set a fix composition at the boundary.
In Console Mode this is similar to the command STATE_VARIABLE_VALUE, but in Graphical Mode this condition is limited to setting a fixed composition.
The flux of selected components is either set to zero or a prescribed activity value.
For Mixed zero flux and activity, and for each independent element selected in the Composition profile, choose either Zero flux or Activity from the lists and enter a value in the field when Activity is selected. The reference state for the components are taken from the System Definer Components tab.
In the field for Activity, enter a formula that the software evaluates during the calculation.
The formula can be:
- A function of the variable TIME
- A constant
The formula must be written with these rules:
- A number must begin with a number (not a dot)
- A number must have a dot or an exponent (E)
The operators + , - , * , / , ** (exponentiation) can be used and with any level of parenthesis.
As shown, the following operators must be followed by () i.e. open and closed parentheses:
- SQRT(X) is the square root
- EXP(X) is the exponential
- LOG(X) is the natural logarithm
- LOG10(X) is the base 10 logarithm
- SIN(X), COS(X), TAN(X), ASIN(X), ACOS(X), ATAN(X)
- SINH(X), COSH(X), TANH(X), ASINH(X), ACOSH(X), ATANH(X)
- SIGN(X)
- ERF(X) is the error function
This is from example D_07: Diffusion Carburization Multiphase.