Region Settings
There should be one unique phase in each region.
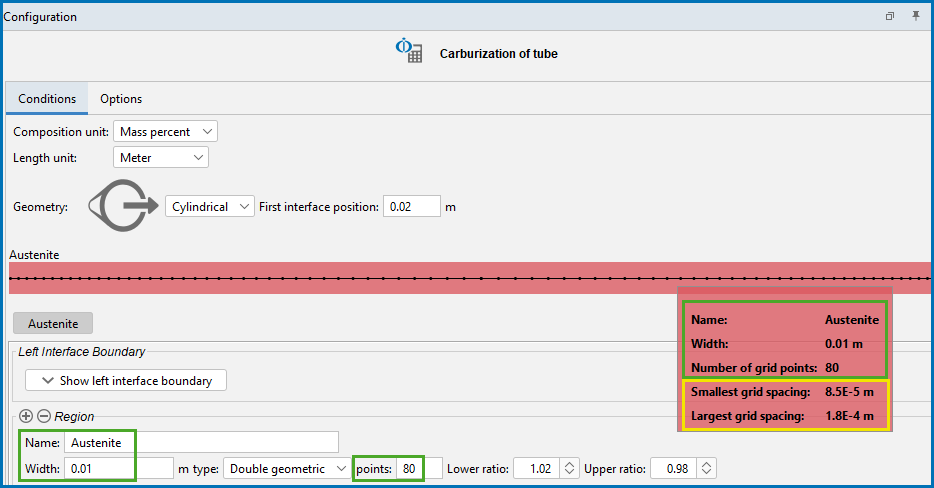
Enter a Name for the region in the field. For example, enter Austenite. This name is automatically updated on the tab and above the grid points graphic.
Enter a numerical value in the Width field. The unit is the one selected for the Length unit.
Select a type of grid:
Automatic is not available when the Composition profiles: Table input is selected. See Composition Profiles.
- Automatic for an automatic grid point distribution. An appropriate grid is generated at the start of the simulation where the grid points are automatically distributed according to the entered composition profile and boundary conditions.
- Linear for an equally spaced grid.
- Geometric for a grid that yields a varying density of grid points in the region.
- Double geometric to have a high number of grid points in the middle or at both ends of a region.
For an Automatic grid type, also choose a grid accuracy level: Coarse, Medium, Fine, or Custom.
The values for the Grid Accuracy settings for each option differ when calculated by Thermo-Calc based on whether it is the Classic or Homogenization model.
- If you are using a Classic model: Fine 75/1.25, Medium 50/1.2, Coarse 25/1.15 (Number of points/Max geometric factor)
- If you are using the Homogenization model: Fine 100/1.03, Medium 80/1.02, Coarse 60/1.01 (Number of points/Max geometric factor)
For Custom, also enter values for:
- max number of points: the maximum number of equidistant points in a region.
- max geometric factor: Value in the geometrical factor in the series determining the distribution of the grid points. A geometrical factor larger than one yields a higher density of grid points at the lower end of the region and a factor is smaller than one yields a higher density of grid points at the upper end of the region.
For Linear, Geometric, or Double geometric grids, enter a numerical value in the points field. The default is 50.
For a Geometric grid, choose or enter a number for the Ratio to determine the distribution. A geometrical factor larger than one yields a higher density of grid points at the lower end of the region and a factor smaller than one yields a higher density of grid points at the upper end of the region.
For a Double geometric grid, specify two geometrical factors. Enter a Lower ratio for the distribution in the lower (left) part of a region, and an Upper ratio for the distribution in the upper (right) part of a region.
The Composition Profiles and Thermal Profile are both set up on the Configuration window for a Diffusion Calculator. These are previewed in the Visualizations window.
Composition Profiles and Diffusion Calculator Thermal Profile
TIP: View a Summary of the Region Grid Point Settings
When working with the Diffusion Calculator in Graphical Mode, you can hover over the grid points on the Configuration window to view additional tooltip details about the region.
The settings information includes the Name of the region (in the example it is renamed to Austenite), the Width of the region, and the number of grid points.
For all types of grids, useful calculated information is included about the Smallest grid spacing and Largest grid spacing points. The information is available to prevent you from setting a combination with too many grid points and a high geometric factor that could lead to unusable grid point spacings.