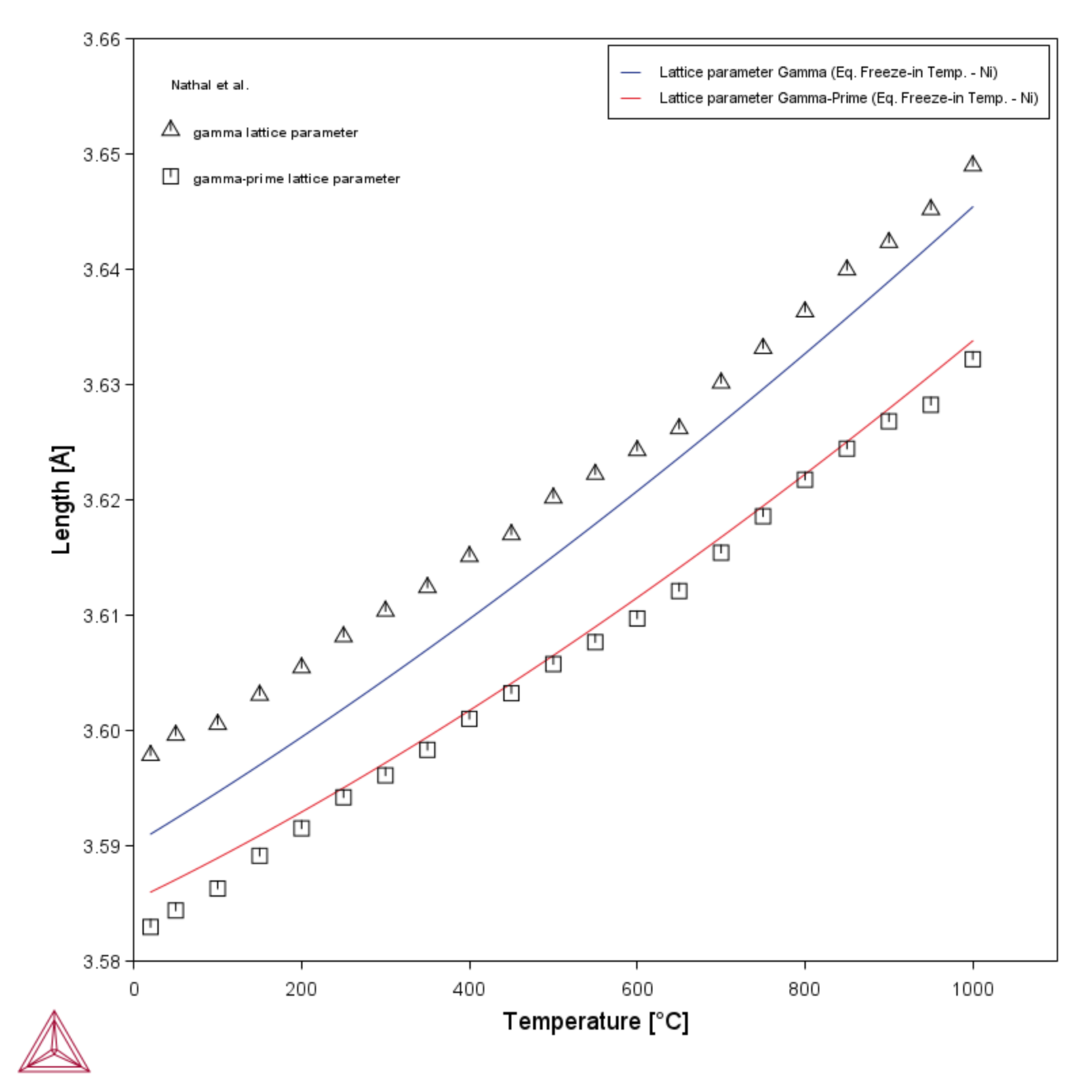
PM_Ni_01: Lattice Parameter of γ/γ'
The example uses the Property Model Calculator with the Equilibrium with Freeze-in Temperature - Ni Model.
Property Model Calculator and About the Equilibrium with Freeze-in Temperature Nickel Property Model
The lattice parameters are measured experimentally for γ/γ' in a Ni0.6Mo0.92Ta12.5Al1.83Ti10.5Cr3.3W alloy.
The thermodynamically stable equilibrium will not be reached for this alloy during the experimental heat treatment; only the phases γ and γ' are noticed in the experiment. The γ/γ' microstructure is in this calculation example assumed to freeze-in at 1000 °C where the phase compositions do not change during cooling to room temperature.
Some of the key settings to note in this example:
- The Subset of phases is selected as Gamma and gamma-prime only to match the experimental observations.
- The Freeze-in temperature is set to 1000 °C.
- A One Axis calculation is used where the evaluation temperatures are within a range of 20 °C to 1000 °C.
- Folder: Property Models → Nickel
- File name:
PM_Ni_01_Lattice_Parameter_of_Gamma_Gamma_Prime.tcu
To run calculations with the Nickel Models requires a valid maintenance license plus licenses for both the TCNI (version 11 and newer) and MOBNI (version 5 and newer) databases. For some Property Models, additional recommendations for the database version to use is indicated in its description. Also see our website to learn more about the Nickel Model Library.
Visualizations
Many of our Graphical Mode examples have video tutorials, which you can access in a variety of ways. When in Thermo‑Calc, from the menu select Help → Video Tutorials, or from the main My Project window, click Video Tutorials. Alternately, you can go to the website or our YouTube channel.
Open the example project file to review the node setup on the Project window and the associated settings on the Configuration window for each node. For some types of projects, you can also adjust settings on the Plot Renderer Configuration window to preview results before performing the simulation. Click Perform Tree to generate plots and tables to see the results on the Visualizations window.
Reference
[1985Nat] M. V. Nathal, R. A. Mackay, R. G. Garlick, Temperature dependence of γ-γ’ lattice mismatch in Nickel-base superalloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. 75, 195–205 (1985).