Surface Tension of Metallic Liquid Alloys Model
In general, for liquid metal alloys, the surface tension is assessed for all the elements and binary systems where experimental data are available. When experimental data are not available, the Butler model [1932But] is used to estimate the composition dependence of the surface tension. The experimental or estimated data are modeled with either the modified Guggenheim model [2019Ver] or the Redlich-Kister-Muggianu sub-regular solution model [1948Red; 1975Mug].
Search the help (press F1) to review the technical information for the database you are using.
Modified Guggenheim Model Description
The surface tension of metallic liquid alloys by the modified Guggenheim model [2019Ver] and is expressed as:
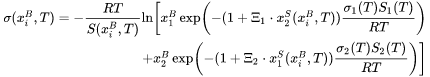
where
-
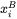 is the bulk composition
is the bulk composition -
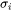 is the surface tension
is the surface tension -
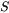 and
and 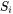 are the total and the partial molar surface of species
are the total and the partial molar surface of species  defined as
defined as
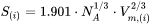
-
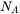 being the Avogadro number and
being the Avogadro number and 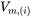 the molar volume of the system or the species
the molar volume of the system or the species  .
. -
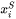 is the composition of
is the composition of  in surface, which is a function of bulk composition and
in surface, which is a function of bulk composition and 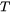 and defined as follows:
and defined as follows:
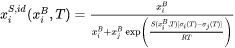
-
 and
and 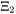 are called damping factors and these parameters are fitted for species 1 and 2 of binary systems.
are called damping factors and these parameters are fitted for species 1 and 2 of binary systems.
The extrapolation to higher-order systems is straightforward. The ideal surface composition for a multicomponent system is:
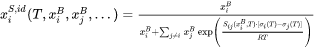
and the surface tension of a multicomponent alloy is obtained from:
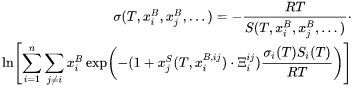
The corresponding variable for surface energy of pure elements is SIGM. For instance, the surface tension of pure A is written as SIGM(LIQUID,A;0). The corresponding X1 and X2 parameters for A-B binary system are respectively written as following:
PARAMETER XI(LIQUID,A,B:0)
PARAMETER XI(LIQUID,A,B:1)
Redlich-Kister-Muggianu Model Description
In the case of using the Redlich-Kister-Muggianu (R-K-M) [1948Red; 1975Mug] sub-regular solution model for modeling the surface tension, the surface tension is given by:
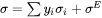
where 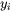 and
and 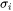 are the site fraction and surface tension for pure component
are the site fraction and surface tension for pure component  , and the excess term is expressed using (R-K) for binary and (R-K-M) for ternary interactions.
, and the excess term is expressed using (R-K) for binary and (R-K-M) for ternary interactions.
The corresponding variable for surface energy of pure elements is SIGM. For instance, the surface tension of pure A is written as SIGM(LIQUID,A;0). The corresponding  parameters for the A-B binary system are written as follows:
parameters for the A-B binary system are written as follows:
PARAMETER SIGM (IONIC_LIQ, A, B; 0)
PARAMETER SIGM (IONIC_LIQ, A, B; 1)
PARAMETER SIGM (IONIC_LIQ, A, B; 2)
Plot Variables (Both Models)
The surface energy can be calculated through various calculations in Console Mode, e.g. a step. The plot variable is SURF(LIQUID).
On the Plot Renderer in Graphical Mode, the plot variable Surface tension can be selected from the axes lists, tabulated and plotted using the quantity names, with options for a specific liquid phase based on the database.
The quantity SURF(LIQUID) can be retrieved, for a liquid phase, e.g. SURF(LIQUID)), via get_value_of() or get_values_of(), from most phase equilibrium calculations in these Software Development Kits (SDKs), for instance,
with_single_equilibrium_calculation(),with_property_diagram_calculation()orwith_batch_equilibrium_calculation().
These can also be accessed in both ThermodynamicQuantity and ScheilQuantity classes. You can, for example, use ThermodynamicQuantity.surface_tension("LIQUID").
Graphical Mode and Console Mode Examples
There are two basic examples included with your software installation and that use demonstration (DEMO) databases.
Search the help (press F1 when in Thermo‑Calc) for brief descriptions of these examples, or browse to the examples located in your installation. From the main menu, Help→ Examples Files:
- Graphical Mode T_11_Surface_tension_in_Cu-Zr.tcu
- Console Mode
tcex56
References
[1932But] J. A. V. Butler, The thermodynamics of the surfaces of solutions. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. A, Contain. Pap. a Math. Phys. Character. 135, 348–375 (1932).
[1948Red] O. Redlich, A. T. Kister, Algebraic Representation of Thermodynamic Properties and the Classification of Solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. 40, 345–348 (1948).
[1975Mug] Y. M. Muggianu, M. Gambino, J. P. Bros, Enthalpy of formation of liquid Bi-Sn-Ga alloys at 723 K, choice of an analytical expression of integral and partial excess quantities of mixing. J. Chim. Phys. 72, 83–88 (1975).
[2019Ver] M. Vermot des Roches, A. E. Gheribi, P. Chartrand, A versatile multicomponent database for the surface tension of liquid metals, Calphad. 65, 326–339 (2019).