Result Quantities: Property Model Abbreviations
When selecting quantities on the Plot Renderer or Table Renderer, the quantity names include an abbreviated name for the Property Model it is associated to. This is useful in particular when you are calculating two or more Property Models that share names for the quantities. The short name identifying the specific Property Model is included in parentheses after the name of the quantity. Below are the full and abbreviated names for each Property Model.
This is not applicable to the Equilibrium Property Model.
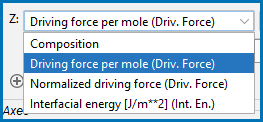
An example of the short names included in parentheses for the Driving Force and Interfacial Energy Property Model quantities. This is from example PM_G_03.
|
Full Name |
Abbreviation |
Model Library |
|---|---|---|
|
Columnar to Equiaxed Transition (CET) |
Col. Eq. Trans. | General |
| Coarsening | Coarsening | General |
| Crack Susceptibility Coefficient | Crack Susc. Coeff. | General |
| Driving Force | Driv. Force | General |
| Equilibrium with Freeze-in Temperature | Eq. Freeze-in Temp. | General |
| Interfacial Energy | Int. En. | General |
| Liquid and Solidus Temperature | Liq. & Sol. Temp | General |
| Phase Transition | Phase Trans. | General |
| Scheil | Scheil | General |
| Spinodal | Spinodal | General |
| T-Zero Temperature | T-Zero Temp. | General |
| Yield Strength | Yield Strength | General |
| Antiphase Boundary Energy | Ant. Bound En. - Ni | Nickel |
| Coarsening Nickel | Coars. -Ni | Nickel |
| Equilibrium with Freeze-in Temperature Nickel | Eq. Freeze-in Temp. - Ni | Nickel |
| Solvus for Ordered Phase | Solv. Ord. Phase - Ni | Nickel |
| Strain-Age Cracking | Strain-Age Crack. - Ni | Nickel |
| Optical Properties | Opt.Prop.- Noble | Noble Metal Alloys |
| Bainite | Bainite | Steel |
| CCT Diagram | CCT Diagr. | Steel |
| Critical Transformation Temperatures | Crti. Transf. Temp. | Steel |
| Ferrite | Ferrite | Steel |
| Martensite Fractions | Mart. Fract. | Steel |
| Martensite Temperatures | Mart. Temp. | Steel |
| Martensitic Steel Strength | Mart. Steel Strength | Steel |
| Pearlite | Pearlite | Steel |
| TTT Diagram | TTT Diagr. | Steel |
| Alloy Strength - Ti | All. Strength - Ti | Titanium |
| Martensite Temperatures - Ti | Mart. Temp. - Ti | Titanium |