T0 Temperature Property Model Settings
T-Zero Temperature is a Property Model available when using the Property Model Calculator in Thermo‑Calc and it calculates the so-called T0 line.
For theory see About the T0 Temperature Property Model.
For examples, see:
Configuration Settings
These settings are found on the Property Model Calculator when T-Zero Temperature is selected under General Models.
When working in the Configuration window, click the Description tab for more information about the Model.
For the details about the Condition Definitions, Calculation Type, Timeout in minutes, Parallel Calculation, and other calculation associated settings, see Property Model Calculator: Configuration Window Settings.
From the First phase list select the applicable phase you want to search for the evaluation of Gibbs energy.
From the Second phase list select the applicable phase you want to search for the evaluation of Gibbs energy.
Use the Energy addition second phase [J/mol] field to include a Gibbs energy addition to the second phase. This allows for inclusion of an energy barrier for martensitic phase transformations.
For an example of this see PM_G_14: Ti-Fe T-Zero Martensite.
From the Condition to vary list select an option to vary when searching for the solution (or root). Up to two solutions can be found. These options are Temperature or those based on the Composition + Composition unit for example Mass percent Fe, Mass percent Cr, Mass percent Ni, and so forth.
When Temperature is the varied condition, 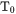 is obtained as a solution. When a specific composition is selected as the condition to vary, then the temperature(s) is calculated when the
is obtained as a solution. When a specific composition is selected as the condition to vary, then the temperature(s) is calculated when the 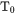 condition is fulfilled. So the resulting temperature is equal to
condition is fulfilled. So the resulting temperature is equal to 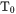 .
.
In most cases the curvature of the Gibbs energies of the two phases is different and results in multiple solutions for 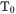 . If you keep the default settings (Condition to vary → Temperature and with no manual search limits) the Property Model Calculator can store up to two solutions. If the solution of interest is not calculated, including Manual search limits and/or changing the condition to vary to one of the listed compositions, allows you to find the solution of interest.
. If you keep the default settings (Condition to vary → Temperature and with no manual search limits) the Property Model Calculator can store up to two solutions. If the solution of interest is not calculated, including Manual search limits and/or changing the condition to vary to one of the listed compositions, allows you to find the solution of interest.
The Manual search limits checkbox is not selected by default and this sets automatic search limits.
Select the checkbox to enter user-defined search limits in the fields. Enter the Lower condition limit and Upper condition limit. Then in the Steps when estimating root(s) field, enter the number of steps in a linear grid when estimating the position(s) of the conditions.
Root means a solution of 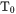 , so a composition and temperature where the Gibbs energies are the same. In other words, it finds the "root(s)" where the two selected phases have equal Gibbs energy.
Think of the "root" as the conditions (temperature, composition) where the Gibbs energy of the two selected phases intersect, i.e. have equal Gibbs energies.
, so a composition and temperature where the Gibbs energies are the same. In other words, it finds the "root(s)" where the two selected phases have equal Gibbs energy.
Think of the "root" as the conditions (temperature, composition) where the Gibbs energy of the two selected phases intersect, i.e. have equal Gibbs energies.
Plot Renderer Settings
Plot Renderer and Plot Renderer: Configuration Settings
When setting up your calculation on the Plot Renderer and/or Table Renderer, the following axis variables are available for the conditions defined on the Property Model Calculator.
When selecting quantities on the Plot Renderer or Table Renderer, the quantity names include an abbreviated name for the Property Model it is associated to. This is useful in particular when you are calculating two or more Property Models that share names for the quantities. The short name identifying the specific Property Model is included in parentheses after the name of the quantity. Below are the full and abbreviated names for each Property Model.
For a list of the abbreviations associated to a Property Model, see Result Quantities: Property Model Abbreviations.
Select from these plot quantities:
- Composition, when the search condition is temperature
- Temperature, when the search condition is composition (in this case temperature is equal to T-Zero.
- T-Zero: The first root (solution) when the search condition is temperature.
- T-Zero - 2nd solution: The second root (solution) when the search condition is temperature.
- Varied condition: The first varied condition regardless of search condition type.
- Varied condition - 2nd solution: The second varied condition regardless of search condition type.