Martensite Temperatures - Ti Property Model Settings
The Martensite Temperatures - Ti Property Model, available with the Property Model Calculator and the Titanium Model Library, calculates the martensite start temperature (Ms) and T-Zero temperatures for Ti-base alloys.
About the Martensite Temperatures - Ti Property Model
For an example see PM_Ti_01: Martensite Temperatures for Ti-Zr
To run calculations with the Titanium Models requires a valid maintenance license plus a license for the TCTI (version 6 and newer) database. For some Property Models, additional recommendations for the database version to use is indicated in its description. Also see our website to learn more about the Titanium Model Library.
Configuration Settings
The settings are found on the Property Model Calculator when Martensite Temperatures - Ti is selected under Titanium Models.
When working in the Configuration window, click the Description tab for more information about the Model.
For the details about the Condition Definitions, Calculation Type, Timeout in minutes, Parallel Calculation, and other calculation associated settings, see Property Model Calculator: Configuration Window Settings.
Additionally note the following about the Temperature setting for this Property Model. You can also select the Annealing checkbox to treat this as the annealing temperature. See details below.
The temperature at which an initial equilibrium is calculated to set the starting composition and internal constitution (in case of ordering) of the parent phase. Should reflect the initial microstructure of the studied alloy. The starting composition and constitution is held fixed throughout the calculation as it is expected that the alloy can not equilibrate during a martensitic transformation.
Select a Martensite phase from the list: HCP ( ,
, 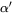 , or
, or 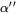 ), B19_PRIME (shape-memory alloys), or B19_ORTHO (shape-memory alloys).
), B19_PRIME (shape-memory alloys), or B19_ORTHO (shape-memory alloys).
- HCP (
 ,
, 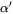 , or
, or 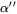 ) is the common choice for alloys such as Ti-6Al-4V and other structural alloys.
) is the common choice for alloys such as Ti-6Al-4V and other structural alloys. - B19_PRIME (shape-memory alloys) for TiNi-based shape-memory alloys.
- B19_ORTHO (shape-memory alloys) for TiNi-based shape-memory alloys. This setting is particularly useful for TiNiCu-based shape-memory alloys.
In the Parent phase energy addition [J/mol] field enter a value in J/mol to add a Gibbs energy shift for the parent phase. This should normally only be used for calculating T-Zero since it might produce unpredictable results for Ms.
The expression can be a function of temperature, T, and composition, w(el) or x(el), for example:
50*T/1000+10*x(Cr)+5*x(Cr)^2
The default is 0 J/mol.
The model initially calculates a global equilibrium for the bulk composition in order to identify the correct parent phase. The temperature condition for this calculation is taken from the Condition Definitions setting.
It is also possible to treat this temperature as the annealing temperature, i.e., that the composition of the parent phase is taken from the equilibrium calculation at this temperature and used as composition conditions.
If the parent phase is the only stable phase, the nominal composition is equal to the parent phase composition. However, for multiphase equilibria, the composition of the parent phase will differ from the build composition.
Select the Annealing checkbox to use the annealing temperature instead of the Temperature set under Condition Definitions.
Plot Renderer Settings
Plot Renderer and Plot Renderer: Configuration Settings
When setting up your calculation on the Plot Renderer and/or Table Renderer, the following axis variables are available for the conditions defined on the Property Model Calculator.
- Temperature
- Ms temperature: Martensite start temperature
- T-Zero temperature