Vertical Sections
Thermodynamic descriptions of core binary, ternary, and quaternary systems are of fundamental importance to the TCS Mg-based Alloys Database (TCMG). Such descriptions are derived from thermodynamic modeling based on phase equilibria data and thermodynamic properties. Once available, these can be used for predicting phase equilibria in the validated composition and temperature space.
Typical phase diagrams are isothermal sections and vertical sections. In these examples, typical vertical sections of several core ternary systems and the Mg-Al-Mn-Zn quaternary system are shown. Such diagrams can be of practical applications as well, e.g. making a preliminary determination of the heating temperature for melting, solution treatment, homogenization, and aging for specific alloys.
Ag-Mg-Sn
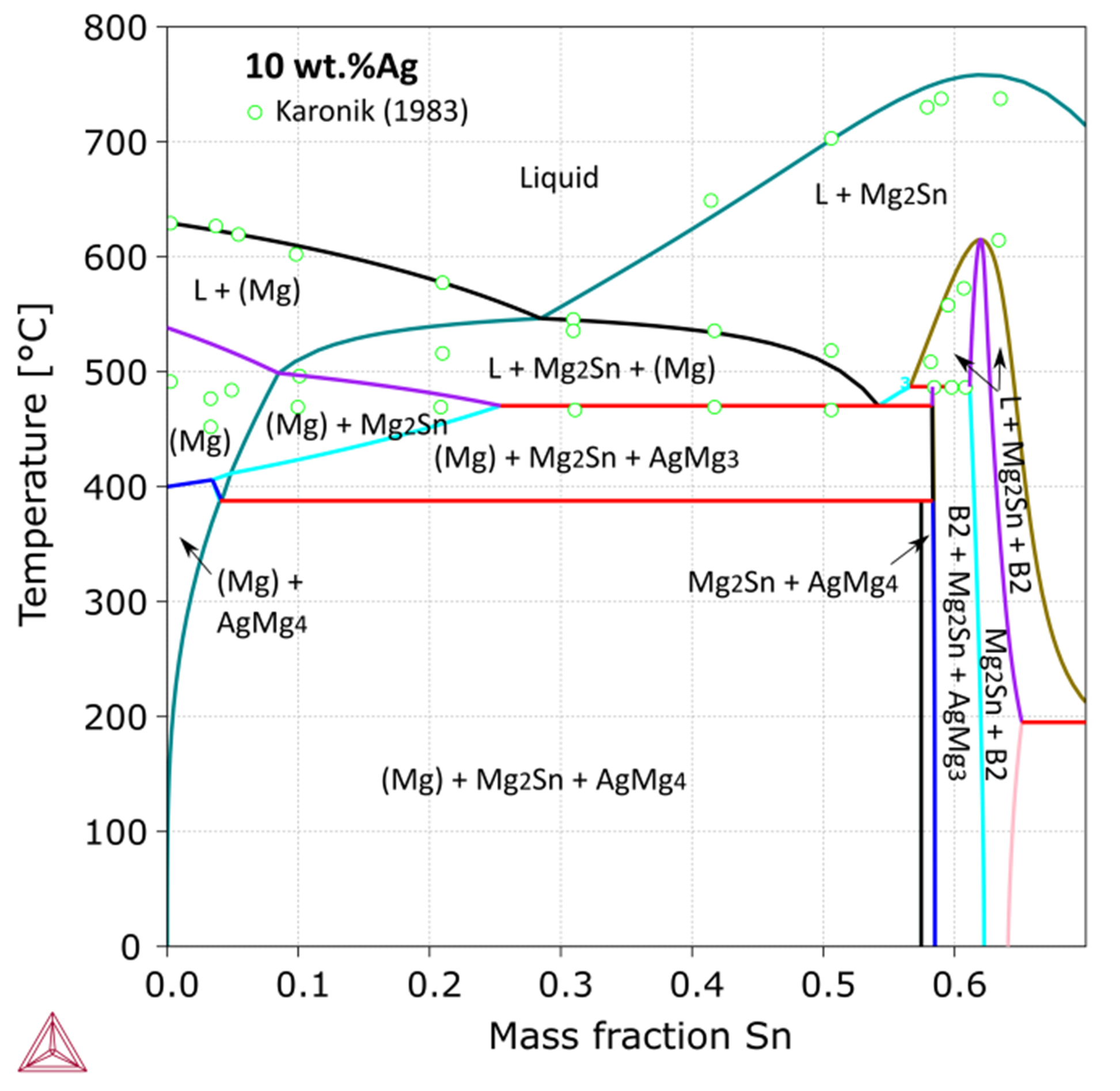
Figure 1: Calculated Ag-Mg-Sn vertical section at 10 wt.% Ag [2018Che], compared with experimental data [1983Kar].
Al-Mg-Sn
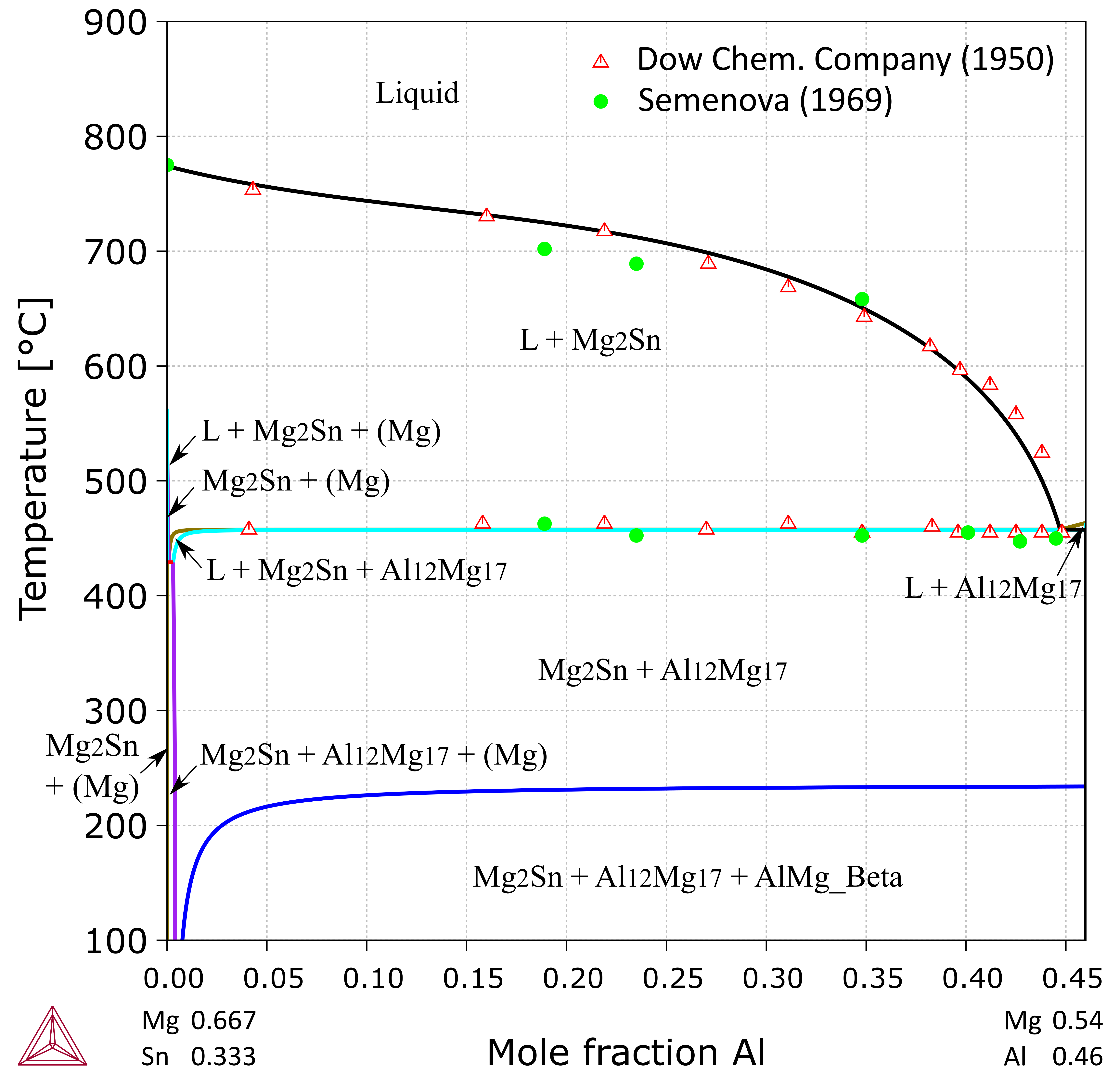
Figure 2: Calculated vertical section from Mg0.667Sn0.333 to Mg0.54Al0.46 (at.%) Experimental data cited in [2007Doe].
Ce-Mg-Mn
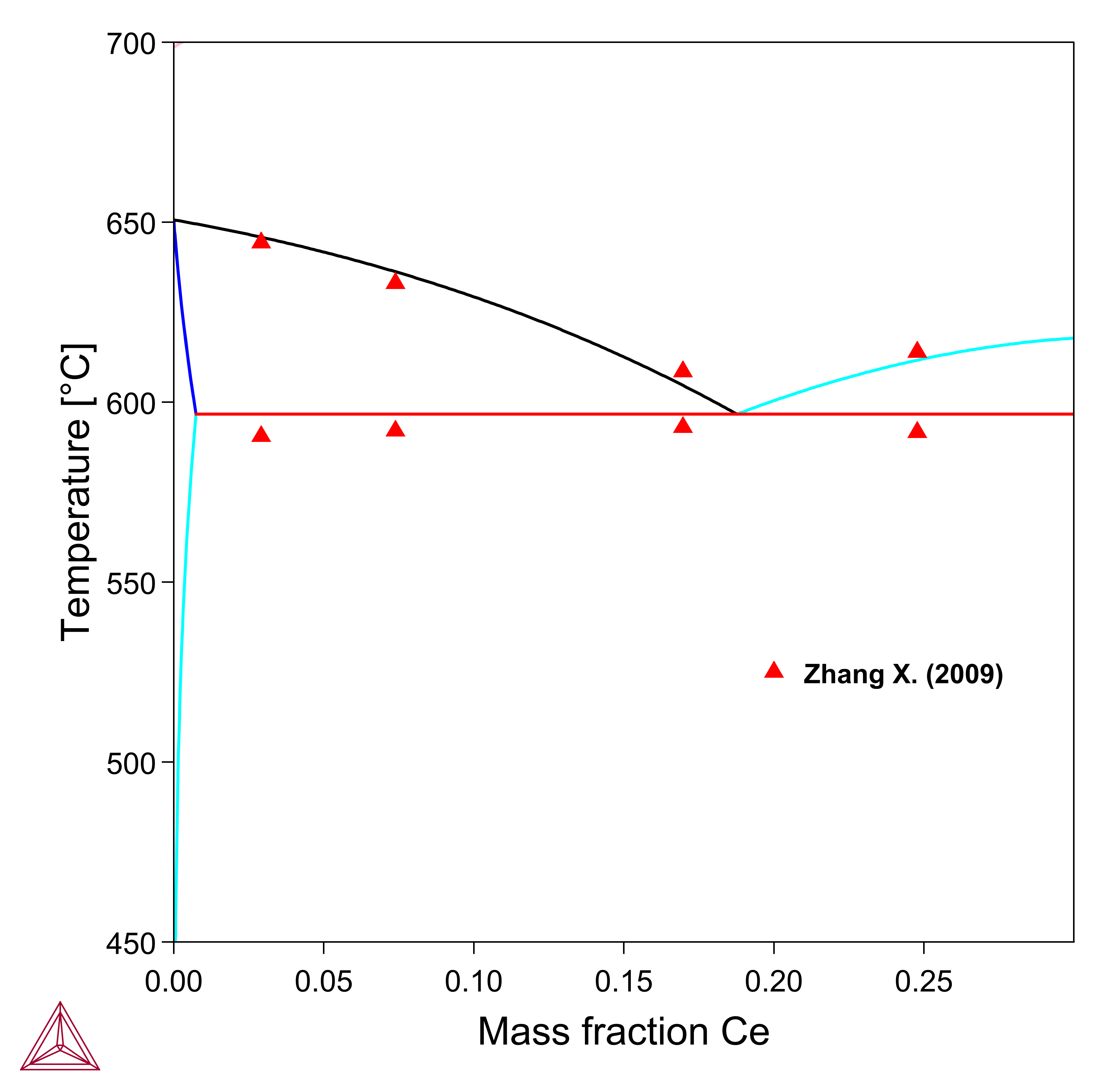
Figure 3: Calculated Ce-Mg-Mn vertical section at 2.5 wt. % Mn, compared with experimental data from [2009Zha].
Mg2Sn-Mg2Zn
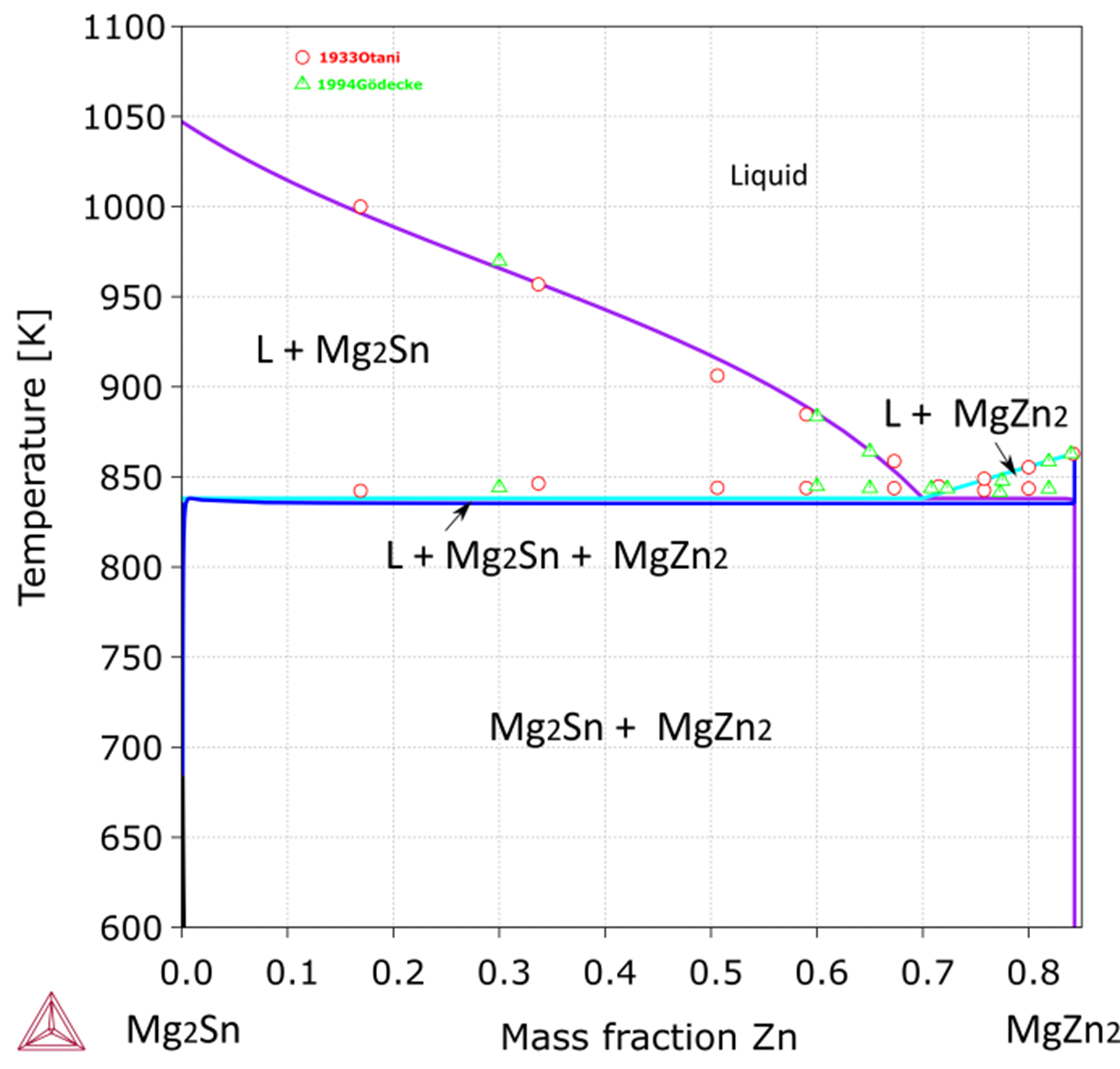
Figure 4: Calculated vertical section from Mg2Sn to MgZn2 [2010Men], compared with experimental data [1933Ota].
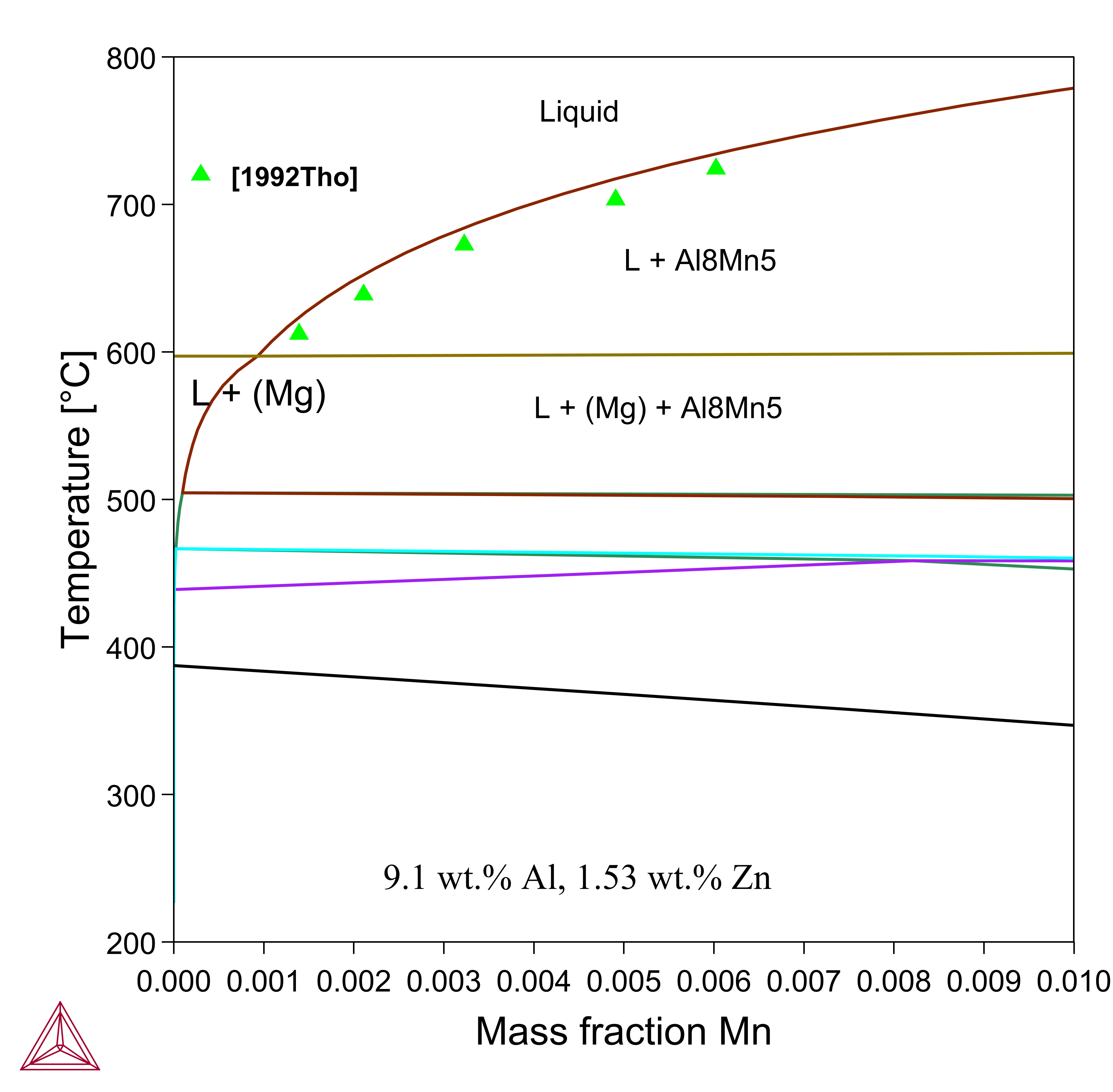
Mg-Al-Mn-Zn
Figure 5: Calculated vertical section at 9.1 wt.% Al -1.53 wt.% Zn with Mn varying from 0 to 1 wt.% in the Mg-Al-Mn-Zn system. The experimental data are from [1992Tho].
References
[1933Ota] B. Otani, Constitution of the Phase Equilibrium Diagram of the Magnesium-Zinc-Tin System (in Japanese), Tetsu-to-Hagane, vol. 19, no. 7, pp. 566–574 (1933).
[1983Kar] V. V. Karonik, V. E. Kolesnichenko, A. A. Shepelev, and G. I. Kand, Magnesium-Silver-Tin Phase Diagram, Met. Splav. na Osn. Tsv. Met. M, no. 78–84 (1983).
[1992Tho] A. Thorvaldsen, C. A. Aliravci, Adv. Prod. Fabr. Light Met. Met. Matrix Comp., in Proceedings of the International Symposium, p. 277 (1992).
[2007Doe] E. Doernberg, A. Kozlov, R. Schmid-Fetzer, Experimental Investigation and Thermodynamic Calculation of Mg-Al-Sn Phase Equilibria and Solidification Microstructures. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 28, 523–535 (2007)
[2009Zha] X. Zhang, D. Kevorkov, I.-H. Jung, M. O. Pekguleryuz, Phase equilibria on the ternary Mg–Mn–Ce system at the Mg-rich corner. J. Alloys Compd. 482, 420–428 (2009).
[2010Men] F. G. Meng, J. Wang, L. B. Liu, and Z. P. Jin, Thermodynamic modeling of the Mg–Sn–Zn ternary system, J. Alloys Compd., vol. 508, no. 2, pp. 570–581 (2010).
[2018Che] H.-L. Chen, Thermodynamic assessment of the Ag-Mg-Sn system in TCMG5, Thermo‑Calc Software (2018).