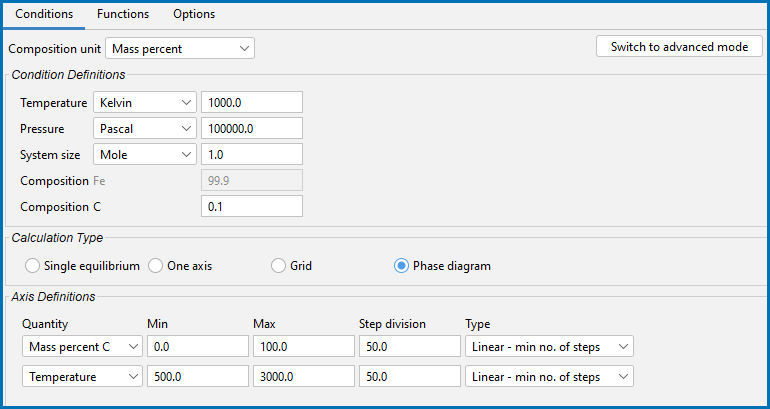
Equilibrium Calculator: Conditions Tab Settings
Conditions and axis variables for the Equilibrium Calculator are set in the Conditions tab on the Configuration window. The tab can be viewed in two modes: Simplified (the default) or Advanced (see About Advanced Mode). The conditions to set depend on the type of calculation.
Equilibrium Calculator: Options Tab Settings
Depending on the calculation type selected, there are also a variety of Plot Types to choose from.
Settings
The following outlines what you can set on the Conditions tab in simplified mode.
Click Switch to Advanced Mode for more options.
Select the Composition unit: Mass percent, Mole percent, Mass fraction, or Mole fraction.
Specify the values (and units) of the state variables: Temperature, Pressure, and System size or any other available lists under Condition Definitions.
Click to select a Calculation Type:
- Single equilibrium (no axes): To calculate a single point. The results from this calculation are displayed in the Event Log.
- One Axis: To vary a quantity on the X-axis.
- Grid: Computes the equilibrium of each grid point in a two-dimensional grid.
- Phase diagram: To calculate in a defined multicomponent heterogeneous system, from one or more initial equilibria. A phase diagram is usually mapped within a specific space that is constructed by two (or more) defined independent mapping axis-variables.
For Single equilibrium, no additional settings are required. Add a Table Renderer to perform the calculation and view the details in the Visualizations window.
When you use the Equilibrium Property Model Settings with the Property Model Calculator, it is the same calculation result as when you are using an Equilibrium Calculator with the Single equilibrium calculation type.
- One Axis: Define the axis variable using these fields and menus: Quantity, Min, Max, Step division, Type, and Step Method.
- Grid: Define the two axis variables using these fields and menus: Quantity, Min, Max, and Number of steps.
- Phase diagram: Define the two axis variables using these fields and menus: Quantity, Min, Max, Step division, and Type.
If the Calculator already has a Plot Renderer as a successor and you change the stepping/mapping quantities, then the quantities represented on the X- and Y-axis are automatically updated in the Plot Renderer.
Depending on the calculation type selected, there are also a variety of Plot Types to choose from.
Enter a Step division and select a Type: Linear - min no. of steps, Linear - max step size, or Logarithmic - scale factor.
- For Linear - min no. of steps, the Step division value specifies a minimum number of steps that is calculated between the minimum and maximum value during the stepping/mapping operation.
- For Linear - max step size, the Step division sets the maximum size of each step. For Logarithmic - scale factor, Step division specifies the scale factor of a logarithmic function that distributes the steps from the initial equilibrium to the minimum and maximum values defined.
From the Step Method list, choose Normal or Separate phases.
- Normal allows a stepping calculation with the chosen independently-varying equilibrium condition (axis-variable). Only the step axis value is changed between each step.
- Separate phases calculates how the Gibbs energy for a number of phases varies for different compositions. This is particularly useful to calculate Gibbs energies for complex phases with miscibility gaps and for an ordered phase that is never disordered (e.g. SIGMA-phase, G-phase, MU-phase, etc.).
Set a fixed Number of steps. The number of steps along with the minimum and maximum values for the axes define a grid. For each grid point an equilibrium is calculated.
About Advanced Mode
Click Switch to Advanced Mode to add and remove conditions as well as set additional axis definitions. However, the number and types of conditions set must still conform to the Gibbs’ phase rule. The Number of missing conditions is field, at the top of the tab shows how many conditions that you have left to set. If the number is negative, then that number of conditions need to be removed.
- Activity of component
- Activity referred to a phase
- Amount of component
- Amount of component in a phase
- Amount of phase
- Chemical potential of a component
- Chemical potential referred to a phase
- Composition
- Enthalpy
- Entropy
- Fix phase
- Gibbs energy
- Helmholtz energy
- Internal energy
- In(activity of component)
- In(activity referred to a phase)
- Pressure
- Site fraction
- System size
- Temperature
- User-defined
- Volume