Ti+3/Ti+4 Ratio
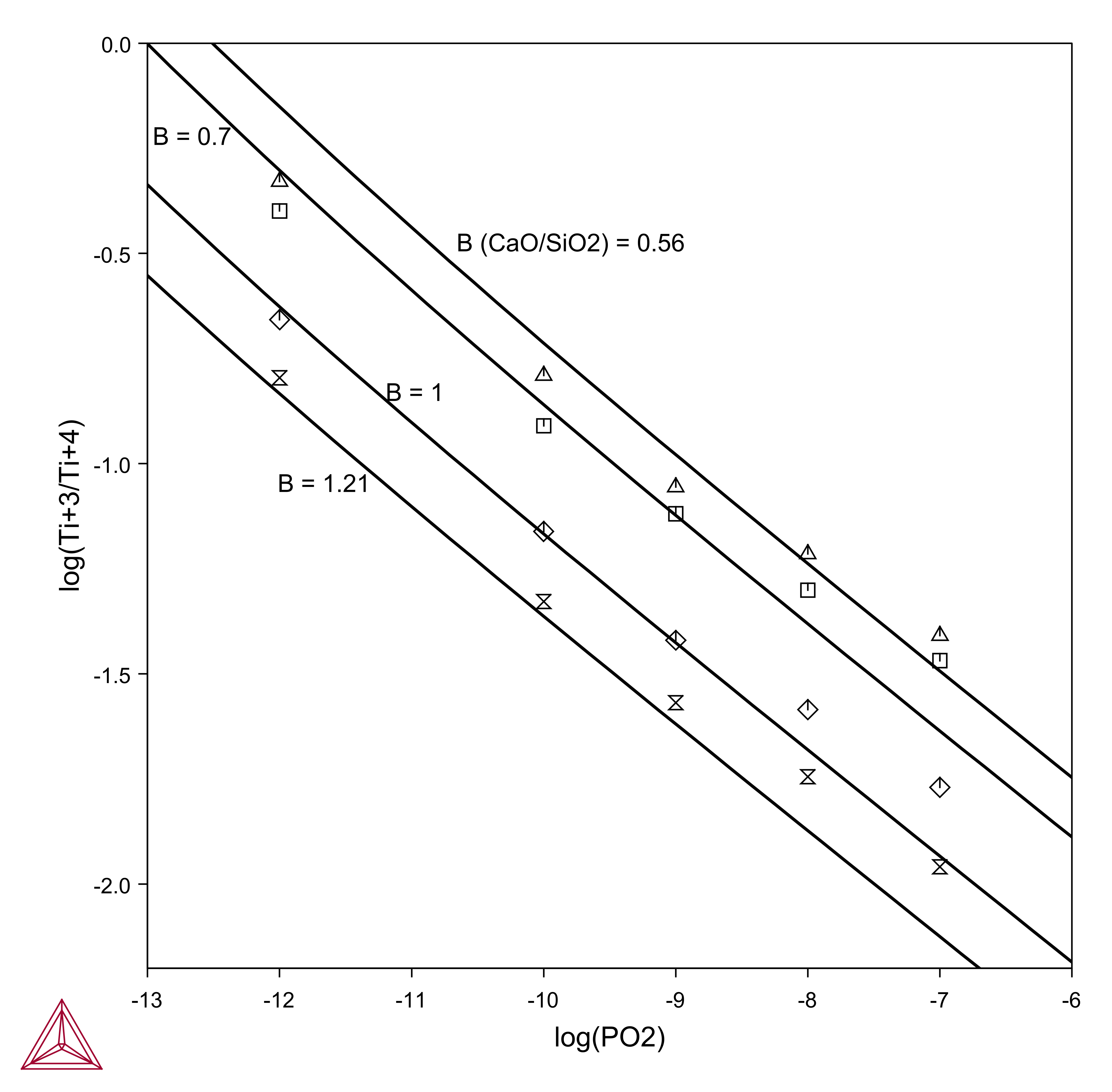
In metallurgical operations, the distribution of titanium between liquid metal and slag, as well as the partitioning among Ti+4, Ti+3 and Ti+2 valency states in the slag, is determined by the oxygen partial pressure, slag composition, and temperature. The oxides associated with the three valencies of titanium are expected to exhibit inherently different properties, affecting both the physical and thermodynamic behavior of slags containing these oxides. Experimental results show that the Ti+3/Ti+4 ratio in CaO-SiO2-TiOx slags increase with decreasing oxygen partial pressure and decreased with increasing CaO/SiO2 ratio and decreasing temperature as shown in this example using the TCS Metal Oxide Solutions Database (TCOX).