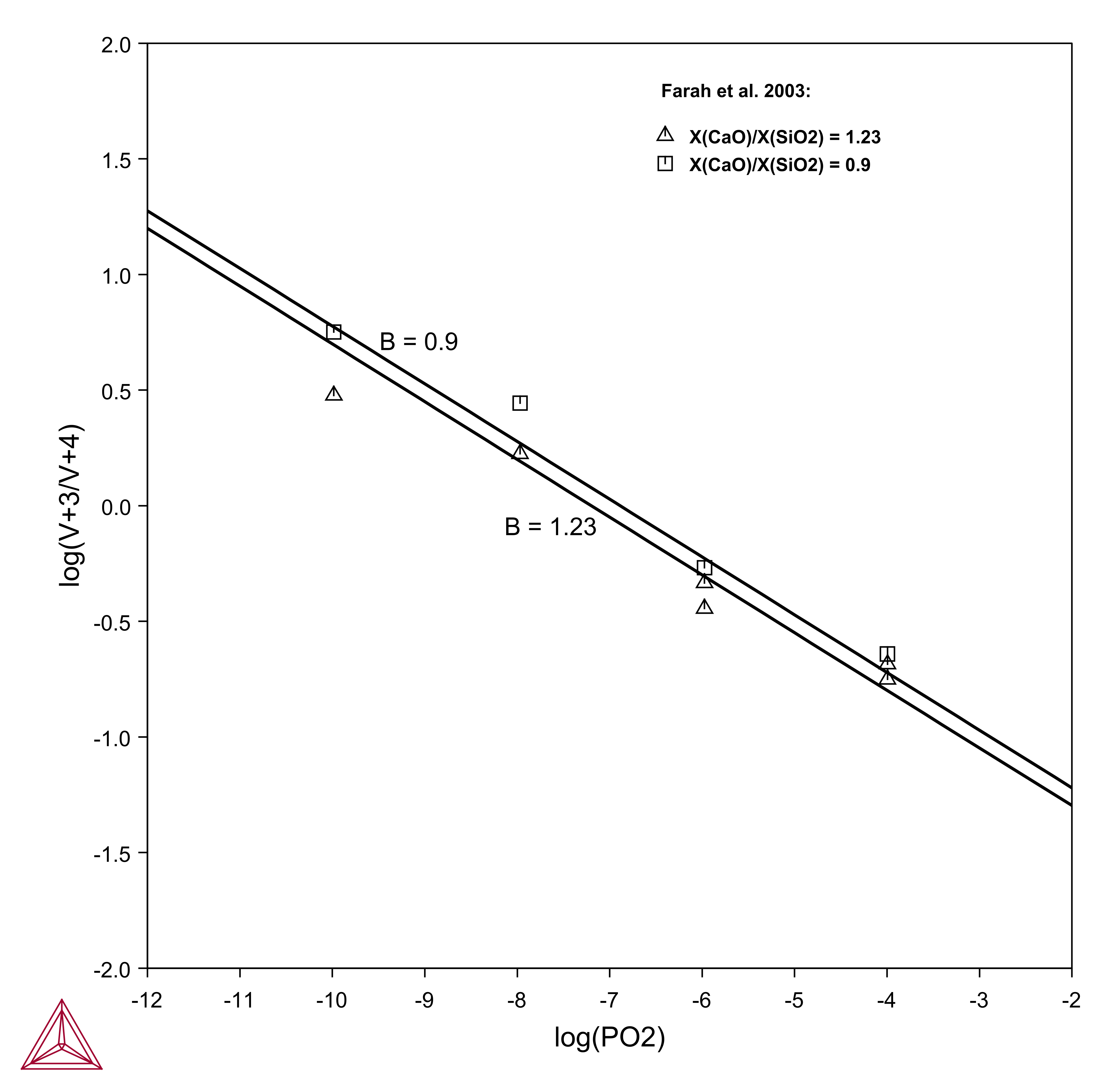
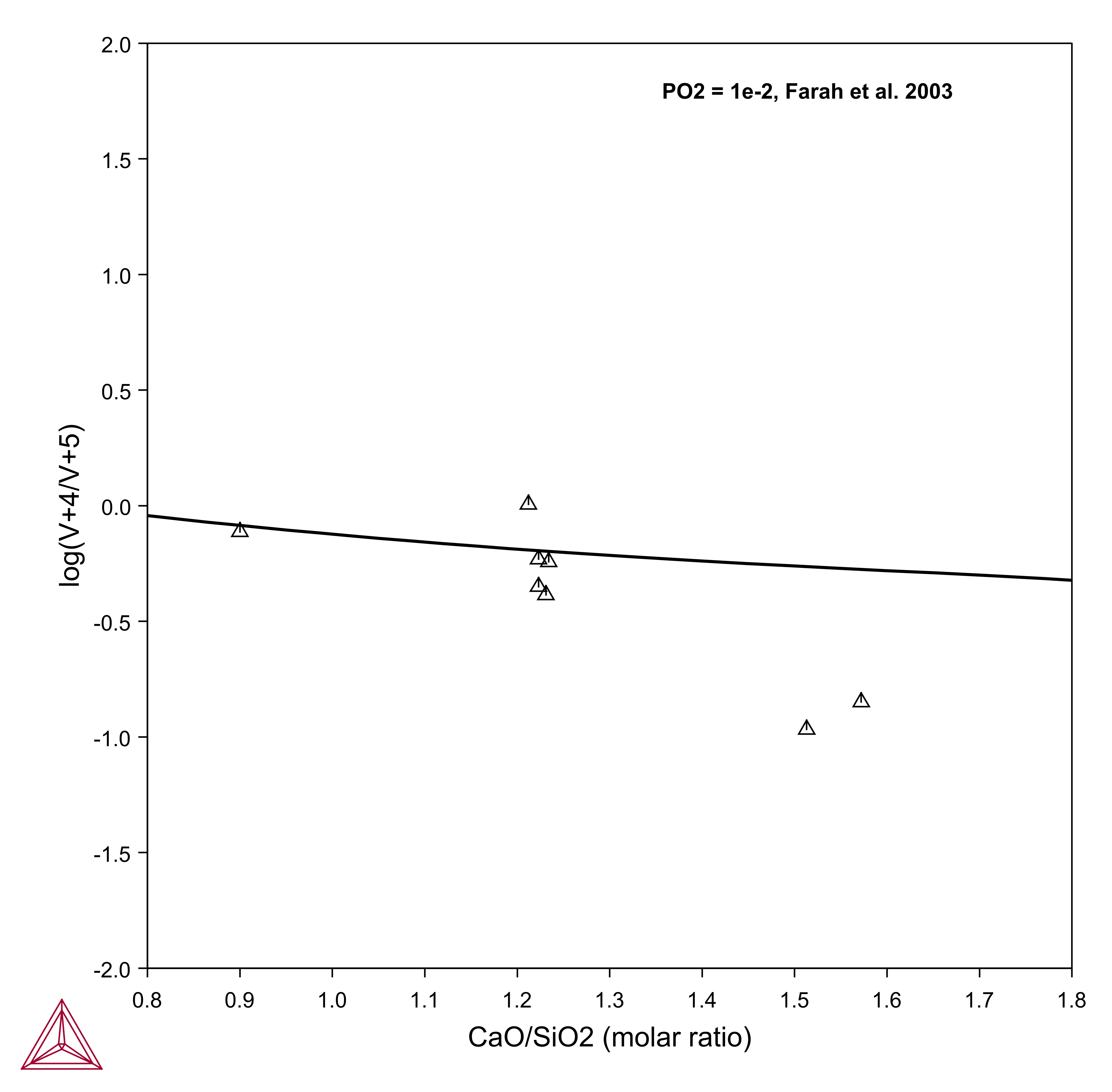
V+3/V+4/V+5 Ratio
Vanadium is a multivalent element which can occur as V+2, V+3, V+4, and V+5. The distribution of vanadium between liquid metal and slag, as well as the partitioning among the different valency states in the slag, is determined by the oxygen partial pressure, slag composition, and temperature.
At the production of ferroalloys, slags can include large quantities of vanadium. In order to understand the activity of vanadium during the process, it is of great importance to know the oxidation behavior, something that can be further understood using the TCS Metal Oxide Solutions Database (TCOX).
Figure 1: Variation of the V+3/V+4 ratio with oxygen partial pressure with different CaO/SiO2 ratios. Calculated at 1600 °C with experimental data.