Residual Element Tin (Sn)
As one of the most common impurity elements in steel, tin (Sn), is brought into the steel through the furnace burden and ferroalloys used during the smelting process. As it is difficult to oxidize during the steelmaking process, it remains an impurity in the steel. For most steel grades, high tin content can seriously deteriorate the physical properties and performance.
Fe-C-Sn and Fe-C-Si-Sn Alloys
The TCS Steel and Fe-alloys Database (TCFE) includes thermodynamic descriptions of many tin (Sn) related systems such as Fe-Sn-X (X=C, Cr, Cu, Mn, Nb, Ni, O, S, Si, W, Zn, Zr), and Al-C-Sn, allowing accurate calculations required to evaluate the effect of Sn content in ferrous alloys. For example, the calculated tin partition coefficient for equilibrium between austenite and liquid for various Fe-C-Sn and Fe-C-Si-Sn alloys is compared with the experimental data in the table below.
For the calculated results, the temperature or the carbon content was slightly changed to ensure an austenite/liquid equilibrium.
| Alloy | Holding T (K) | Experimental | Calculated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe-1.71C-0.76Sn (a) | 1676 | 0.28 [1991Ima] | 0.33 |
| Fe-2.42C-1.64Sn (a) | 1613 | 0.37 [1991Ima] | 0.39 |
| Fe-2.91C-1.03Sn (a) | 1586 | 0.42 [1991Ima] | 0.43 |
| Fe-2.72C-0.52Sn | 1573 | 0.41 [1991Ima] | 0.45 |
| Fe-3.26C-0.46Sn | 1523 | 0.49 [1991Ima] | 0.52 |
| Fe-3.58C-1.1Sn | 1485 | 0.63 [1991Ima] | 0.59 |
| Fe-3.77C-0.43Sn | 1443 | 0.73 [1991Ima] | 0.69 |
| Fe-4.02C-1.66Sn (a) | 1418 | 0.84 [1991Ima] | 0.72 |
| Fe-3.92C-1.01Sn-1.45Si (a) | 1426 | 0.58 [1984Tan] | 0.52 |
| Fe-3.54C-1.53Sn-1.49Si (a) | 1484 | 0.46 [1984Tan] | 0.44 |
| Fe-2.53C-1.37Sn-1.26Si | 1558 | 0.32 [1984Tan] | 0.38 |
| Fe-2.07C-1.50Sn-1.41Si (a) | 1623 | 0.28 [1984Tan] | 0.31 |
Fe-C-Sn
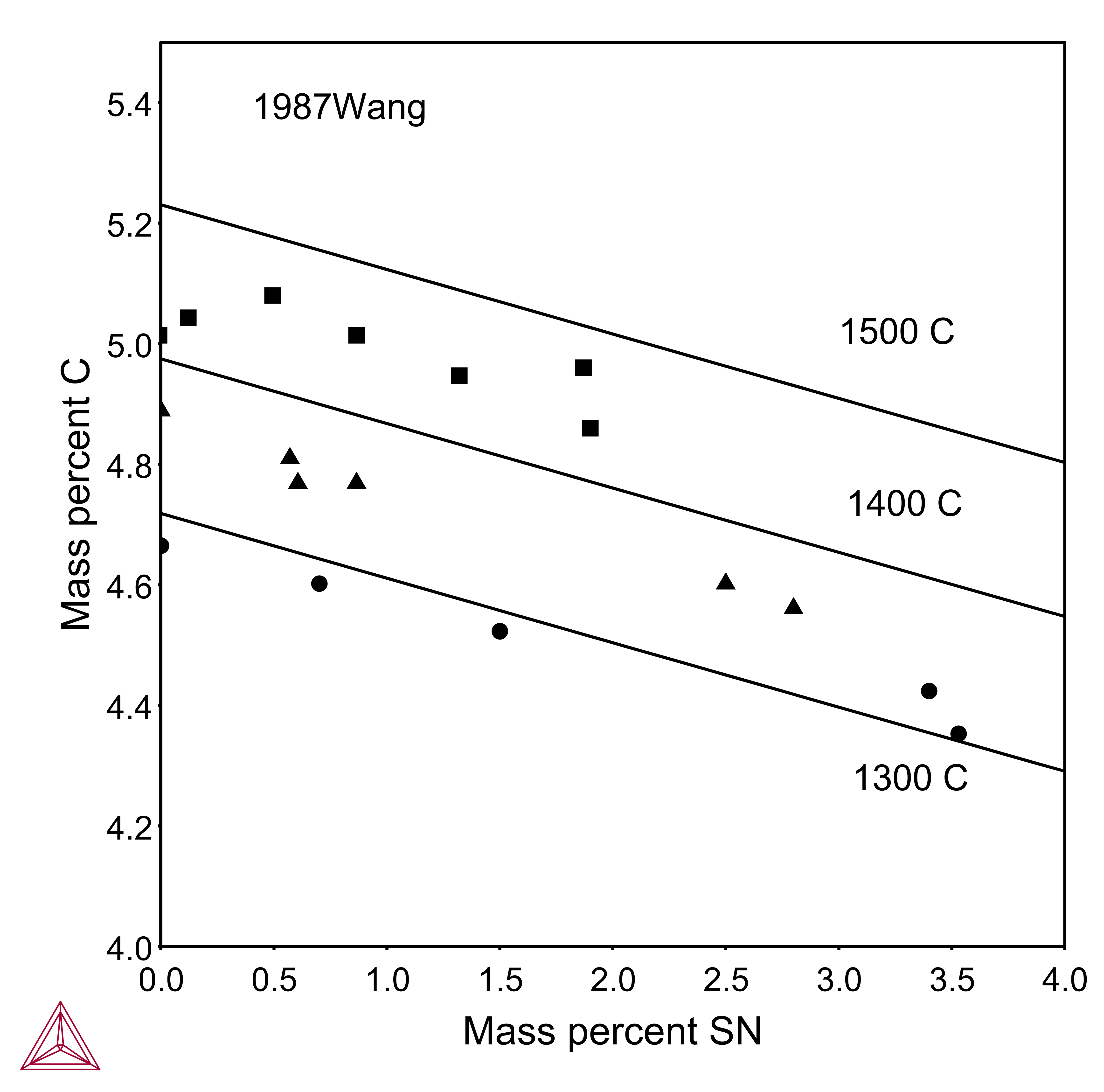
Another example is given below by comparing the measured and calculated carbon solubility limits in Fe-C-Sn liquid at various temperatures for tin content up to 3.5 mass percent.
Figure 1: Comparing the measured [1987Wan] and calculated carbon solubility limits in Fe-C-Sn liquid at various temperatures for tin content up to 3.5 mass percent.
References
[1984Tan] T. Tanaka, Ph.D. thesis, Thermodynamics of the Equilibrium Distribution of Solute Elements Between Solid and Liquid Phases in Iron Alloys, Osaka University Knowledge Archive, 1984.
[1987Wan] Z. Wang, L. Wang, T. Du, Study of the Thermodynamic Properties of Fe-C-Sn, Fe-C-Pb, Fe-C-Pb-Ce Liquid Solutions. J. Iron Steel Res. 7, 99–106 (1987), (in Chinese) (abstract in English).
[1991Ima] N. Imai, T. Tanaka, T. Yuki, T. Iida, Z. Morita, Equilibrium Distribution of Sn between Solid and Liquid Phases in Fe-Sn and Fe-C-Sn Alloys. Tetsu-to-Hagane. 77, 224–230 (1991).