Molar Volume and Density
The TCS High Entropy Alloys Database (TCHEA) includes molar volume information for all phases, which allows calculation of volume, thermal expansion, and density vs. composition and temperature. It can be used for design, and as inputs to other codes e.g. the finite element method (FEM).
|
|
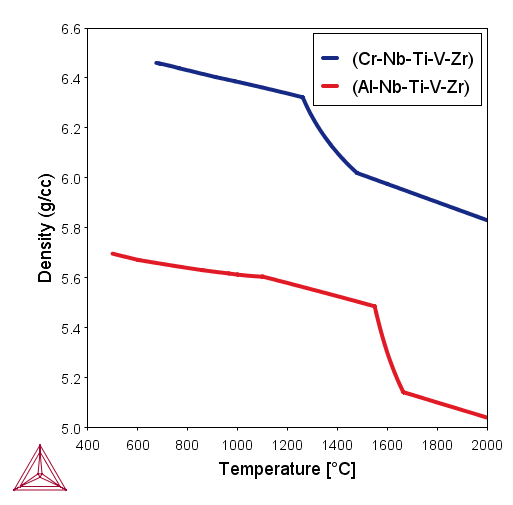
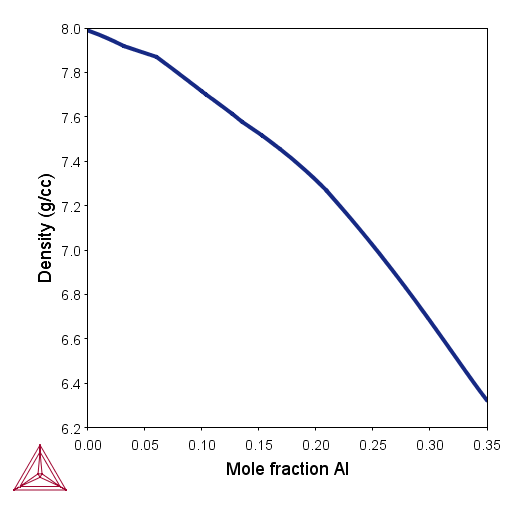
Figure 1: Calculated density of HEAs. (a) Density of CrNbTiVZr and AlNbTiVZr HEAs at various temperatures. The measured room temperature density is 6.57 g/cc for CrNbTiVZr [2013Sen] and 5.79 g/cc for AlNbTiVZr [2015Ste]. (b) Density of AlxCoCrFeNi HEAs at 400°C.
The following table shows the experimental and calculated densities of some BCC HEAs.
|
As-cast HEAs |
HfNbTaTiZr |
MoNbTaVW |
MoNbTaW |
AlCrTiV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Phase Exp (Calc) |
BCC (BCC) |
BCC (BCC) |
BCC (BCC) |
B2 (B2) |
|
Density, g/cm3 Exp (Calc) |
9.94 (9.92) |
12.36 (12.35) |
13.75 (13.80) |
5.06 (5.04) |
|
Experimental reference |
[2011Sen] |
[2010Sen] |
[2010Sen] |
[2017Qiu] |
The following table shows the calculated lattice parameter and density compared to experimental data. Calculation was made at 673K with experimental data from [2018Lap].
|
|
LP Exp. (nm) |
LP Cal. (nm) |
Density Exp. (g/cm3 | Density Cal. (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
CrFeCoNi |
0.357 |
0.359 |
8.1 |
8.03 |
|
CrCoNi |
0.357 |
0.359 |
8.2 |
8.08 |
|
CrFeNi |
0.359 |
0.360 |
7.9 |
7.88 |
|
FeCoNi |
0.358 |
0.359 |
8.4 |
8.30 |
|
MnCoNi |
0.360 |
0.363 |
8.1 |
7.91 |
|
MnFeNi |
0.362 |
0.365 |
7.9 |
7.81 |
|
CoNi |
0.354 |
0.356 |
8.8 |
8.62 |
References
[2010Sen] O. N. Senkov, G. B. Wilks, D. B. Miracle, C. P. Chuang, P. K. Liaw, Refractory high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics. 18, 1758–1765 (2010).
[2011Sen] O. N. Senkov, J. M. Scott, S. V Senkova, D. B. Miracle, C. F. Woodward, Microstructure and room temperature properties of a high-entropy TaNbHfZrTi alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 6043–6048 (2011).
[2013Sen] O. N. Senkov, S. V Senkova, D. B. Miracle, C. Woodward, Mechanical properties of low-density, refractory multi-principal element alloys of the Cr–Nb–Ti–V–Zr system. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 565, 51–62 (2013).
[2015Ste] N. D. Stepanov, N. Y. Yurchenko, D. G. Shaysultanov, G. A. Salishchev, M. A. Tikhonovsky, Effect of Al on structure and mechanical properties of Al x NbTiVZr ( x = 0, 0.5, 1, 1.5) high entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 31, 1184–1193 (2015).
[2017Mao] H. Mao, H.-L. Chen, Q. Chen, TCHEA1: A Thermodynamic Database Not Limited for “High Entropy” Alloys. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 38, 353–368 (2017).
[2017Qiu] Y. Qiu, Y. J. Hu, A. Taylor, M. J. Styles, R. K. W. Marceau, A. V. Ceguerra, M. A. Gibson, Z. K. Liu, H. L. Fraser, N. Birbilis, A lightweight single-phase AlTiVCr compositionally complex alloy. Acta Mater. 123, 115–124 (2017).
[2018Lap] 1. G. Laplanche, P. Gadaud, C. Bärsch, K. Demtröder, C. Reinhart, J. Schreuer, E. P. George, Elastic moduli and thermal expansion coefficients of medium-entropy subsystems of the CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 746, 244–255 (2018).