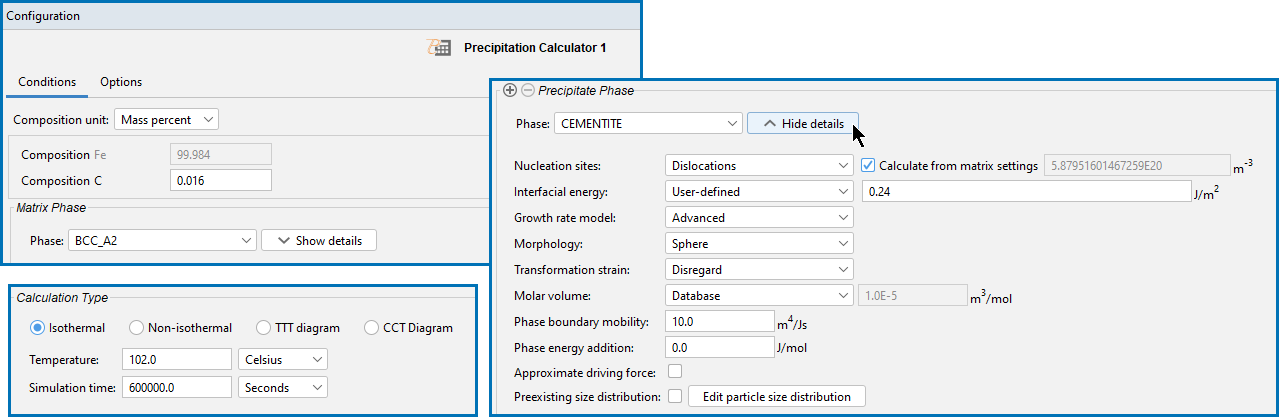
Precipitation Calculator: Matrix Phase Settings
Below are details about the settings available for the Composition and Matrix Phase, which is selected from the Conditions tab on the calculator Configuration window.
There are additional Conditions tab settings described for the Precipitate Phase and Calculation Type.
There are three distinct settings areas for the Configuration window for example P_04_Precipitation_Fe-C_Cemetite. In this case, Show Details is expanded to show the Precipitate Phase settings.
You can change these settings locally for a specific Calculator or globally for some defaults in the Options window (a different location than the tab).
To open the Options window:
- Windows: Select Tools →
 Options.
Options. - Mac: Select Thermo-Calc <version> → Preferences or Settings or press <⌘> on the keyboard.
then click the Graphical Mode tab and the Precipitation node in the tree.
Click Show Details to view some of the additional settings listed below. You can also set the default to display in Phase view mode on the Options window then click the Graphical Mode tab and the Precipitation node in the tree. Click Hide Details to hide the information.
Composition Settings
Select the Composition unit: Mass percent, Mole percent, Mass fraction, or Mole fraction.
Matrix Phase Settings
Selecting the Disordered Phase as a Matrix Phase
Only phases with kinetic data can be selected as the matrix phase. If the list is empty, go to the System Definer to confirm that both thermodynamic and kinetic databases are selected and defined.
Choose a Phase from the list. The list is based on the settings for the System Definer. When setting up a system, choose a matrix phase with kinetic data available in the database.
See Homogeneous Nucleation for theory.
Choose Disregard to ignore the elastic properties.
Default elastic constants for Isotropic or Cubic are based on the major element of the alloy system. The elastic properties can affect nucleation rate, nuclei size, and particle shape.
- For Isotropic, enter values for Shear modulus (in GPa) and Poisson's ratio as required.
- For Cubic, enter values for c11, c12, and c44 as required.
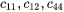 are the elastic constants.
are the elastic constants.
Use the Database value (if the molar volume for the phase is defined in the thermodynamic database) or select User-defined to enter another value in m3/mol.
If you select the Grain growth checkbox, see the separate Grain Growth Settings section for details.
If the Grain growth checkbox is NOT selected then this version of the Grain size section is available in order for the Average diameter of the grain size to be entered.
Grain size is the "diameter" of a grain. The Grain size value changes the available nucleation sites when Grain boundaries, Grain edges, or Grain corners is selected along with Calculate from matrix settings in the Precipitate Phase. Enter a numerical value and choose a unit from the list. The default is 1.0E-4 m.
See Precipitation Morphology and The Number of Available Heterogeneous Nucleation Sites for theory.
For an elongated grain with a minor axis and a major axis, one may use the minor axis as grain size and the major/minor ratio as the grain aspect ratio to characterize the grain. The Grain aspect ratio value also changes the available nucleation sites when Grain boundaries, Grain edges, or Grain corners is selected along with Calculate from matrix settings in the Precipitate Phase. Enter a numerical value. The default is 1.0.
If the Grain growth checkbox is selected, the aspect ratio is fixed at 1.0 and can not be changed. See Grain Growth Settings.
See Precipitation Morphology and The Number of Available Heterogeneous Nucleation Sites for theory.
The Dislocation density value changes the available nucleation sites when Dislocations is selected along with Calculate from matrix settings in the Precipitate Phase. Enter a numerical value. The default is 5.0E12 m-2.
See Precipitation Morphology and The Number of Available Heterogeneous Nucleation Sites for theory.
The Mobility adjustment parameters modify the atomic mobility data from a database.
Choose Same for all elements, which applies the adjustment to all elements, or Per element to adjust to each individual element. Then for the following settings, enter one set of values for Same for all elements, or individually for Per element.
- Prefactor (unitless) is a parameter that multiplies to the mobility data from a database. This value scales the mobility by a constant amount. This can be useful, for example, when the material has a higher than normal vacancy concentration at the start of the precipitation simulation. (e.g. from a prior solutionizing and quenching treatment).
- The Activation energy (J/mol) is a value that adds to the activation energy of mobility data from a database. This value scales the mobility by a temperature-dependent amount. Similar usage as the Mobility adjustment >Prefactor setting.
Grain Growth Settings
Select the Grain growth checkbox to use this to calculate the temporal evolution of grain size distribution (GSD). The grains are assumed of spherical morphology when modeling the growth rates. Nucleation is not considered, thus an initial GSD is necessary to start the simulation.
After selecting the checkbox, there are additional settings made available as described in this section.
This checkbox is not available when a TTT diagram or CCT diagram Calculation Type is selected.
See Normal Grain Growth and Zener Pinning for theory.
When the Grain growth checkbox is selected, then this version of the Grain size settings section is available. This is where you access the grain Size distribution settings.
Click Edit grain size distribution to open the Size distribution settings window. In this window, you can edit the parameters and generate a graph comparing the radius and number density for initial grains.
Select a Length unit: Meter, Micrometer, Nanometer, or Ångström.
Select a Distribution: Normal, Log normal, or From file.
- If Normal or Log normal is selected, enter values for Mean radius and Std (standard deviation). The default Std is different for each choice.
- If Hillert is selected, enter a value for the Mean radius.
- If From file is selected, click Import and navigate to the file containing the required information and click Open. This file can be in .xls, .xlsx, .csv or .txt formats. The file should consist of two columns with values where the first column contains radius data and the second contains number density data.
A similar setup can also be found in the Particle Size Distribution (PSD).
Once the size distribution is defined, click Generate to view or update the graph comparing the radius and number density for initial grains.
This setting is available when the Grain growth checkbox is selected.
Enter a value for the Grain boundary energy. The default is 0.5 J/m2.
See Normal Grain Growth for theory.
This setting is available when the Grain growth checkbox is selected.
The Prefactor (m4/Js) is a parameter that represents the magnitude of the grain boundary motion.
The Activation energy (J/mol) is a parameter that describes the temperature dependence of the grain boundary mobility.
See Grain Boundary Mobility Values for theory and recommended values.
This setting is available when the Grain growth checkbox is selected.
Select the Zenner pinning checkbox to consider the effect of precipitates on inhibiting normal grain growth. When this checkbox is selected, there are additional settings available in the Precipitate Phase section.
See Zener Pinning for theory.