Miscibility Gaps
Miscibility gaps are frequently found in, for example, silicate systems in the liquid slag phase.
Also see the Fe-Si-O system example.
Metastable miscibility gaps in the liquid phase can also be calculated as is shown in this example using the TCS Metal Oxide Solutions Database (TCOX).
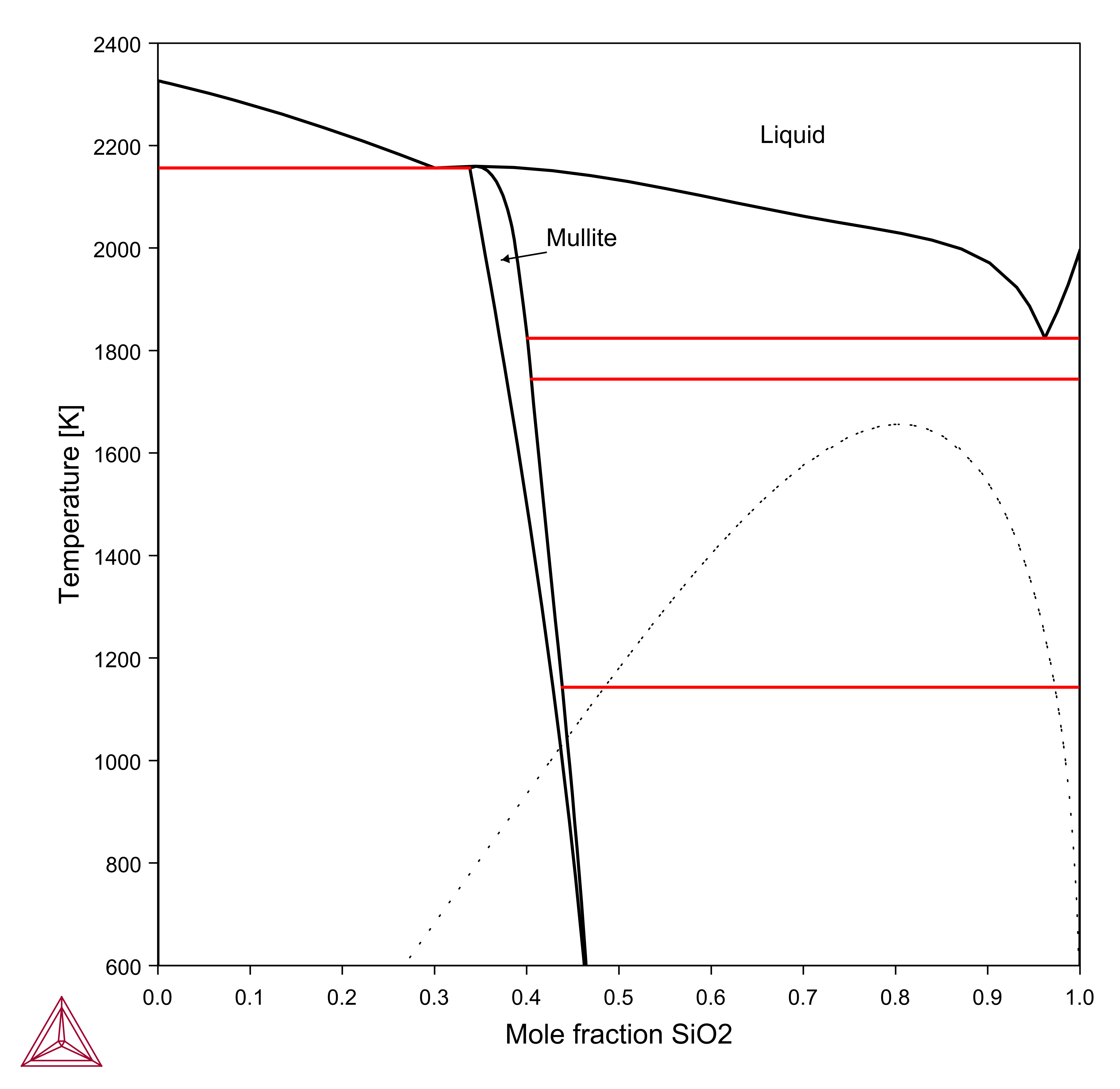
Figure 1: Calculated Al2O3-SiO2 phase diagram. Dashed curve is a metastable liquid miscibility gap [1989aHil; 2007Mao].
Miscibility gaps can also be found in solid phases, both stable and metastable.
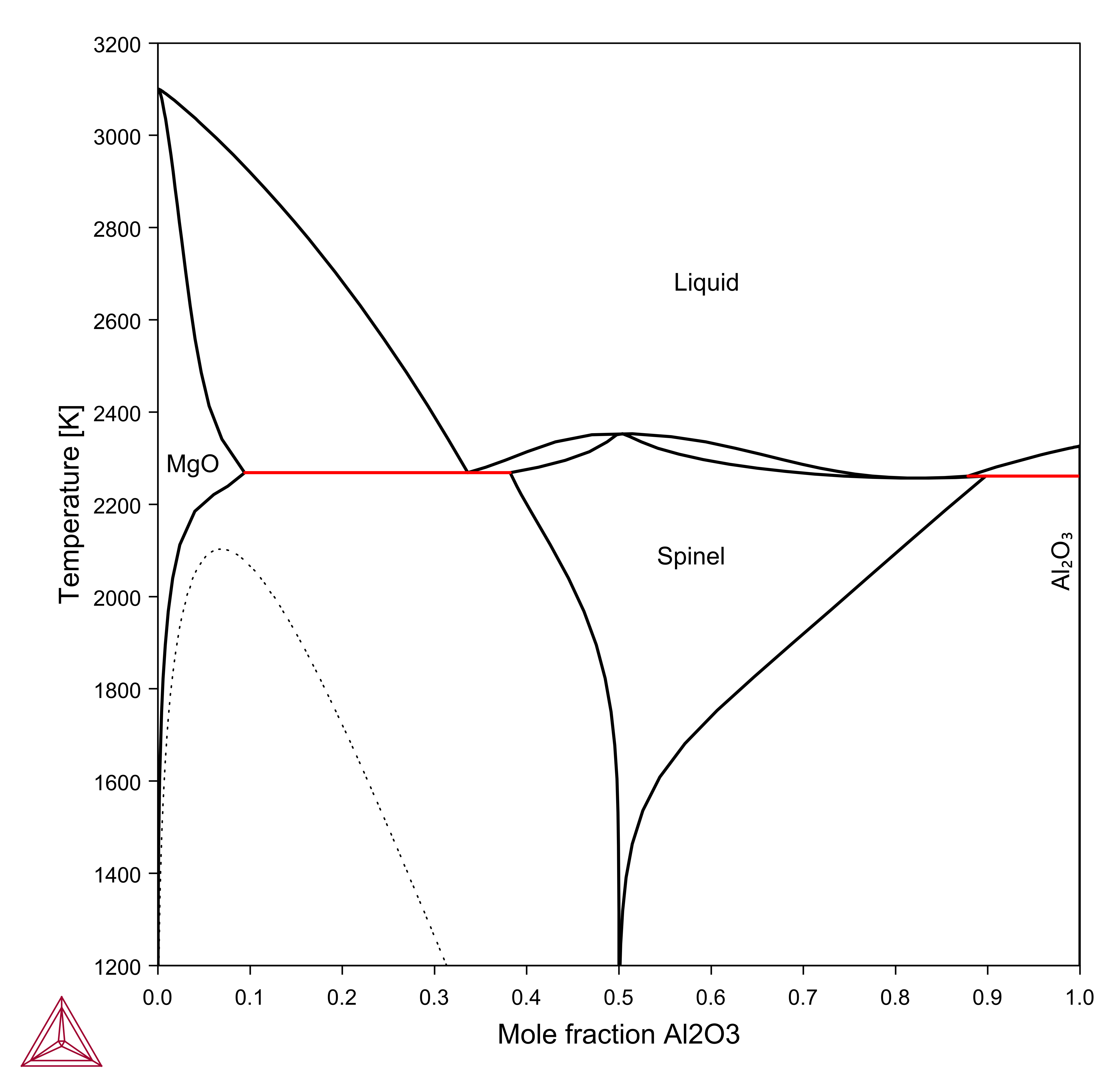
CaO and MgO both have the NaCl structure and are modeled as the same phase: halite. These have some mutual solubility and MgO dissolves some Al2O3.
Figure 2: Calculated MgO-Al2O3 phase diagram. Dashed curve is a calculated metastable miscibility gap in MgO [1992Hal; 2004Mao].
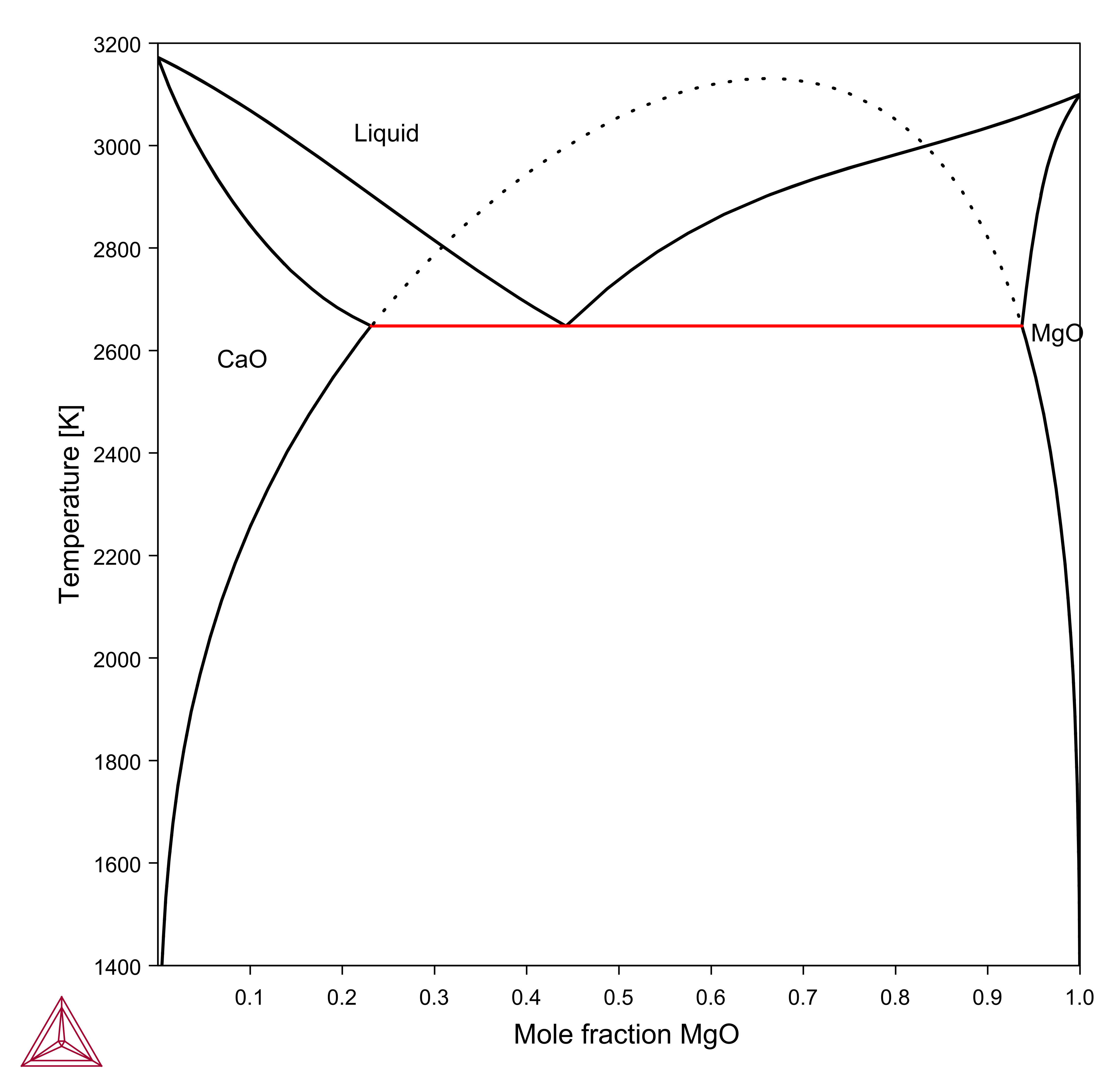
Figure 3: Calculated CaO-MgO phase diagram. Dashed curve is a calculated metastable miscibility gap [1989bHil].
References
[1989aHil] M. Hillert, B. Sundman, X. Wang, A Thermodynamic Evaluation of the Al2O3 -SiO2 System, Trita-Mac. 402, 24 (1989).
[1989bHil] M. Hillert, X. Wang, Thermodynamic calculation of the CaO-MgO system, Calphad. 13, 267–271 (1989).
[1992Hal] B. Hallstedt, Thermodynamic Assessment of the System MgO-Al2O3, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 75, 1497–1507 (1992).
[2004Mao] H. Mao, M. Selleby, B. Sundman, A re-evaluation of the liquid phases in the CaO–Al2O3 and MgO–Al2O3 systems, Calphad. 28, 307–312 (2004).
[2007Mao] H. Mao, M. Selleby, Thermodynamic reassessment of the Si3N4–AlN–Al2O3–SiO2 system—Modeling of the SiAlON and liquid phases, Calphad. 31, 269–280 (2007).