Vertical Sections
Vertical sections can be calculated in different ways. The components can be redefined to match the endmembers, or you can find a condition that matches the section, as shown in these examples using the TCS Metal Oxide Solutions Database (TCOX).
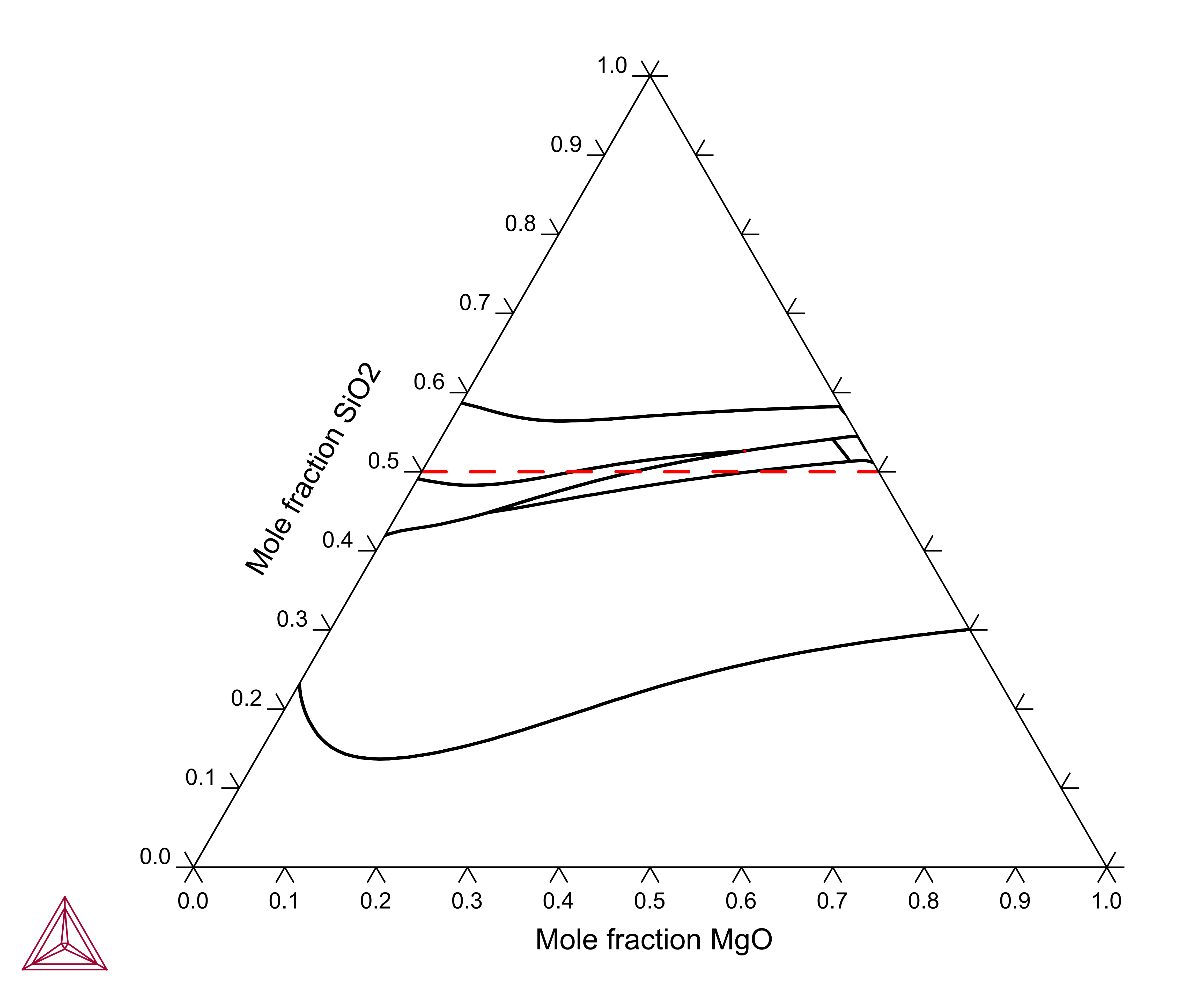
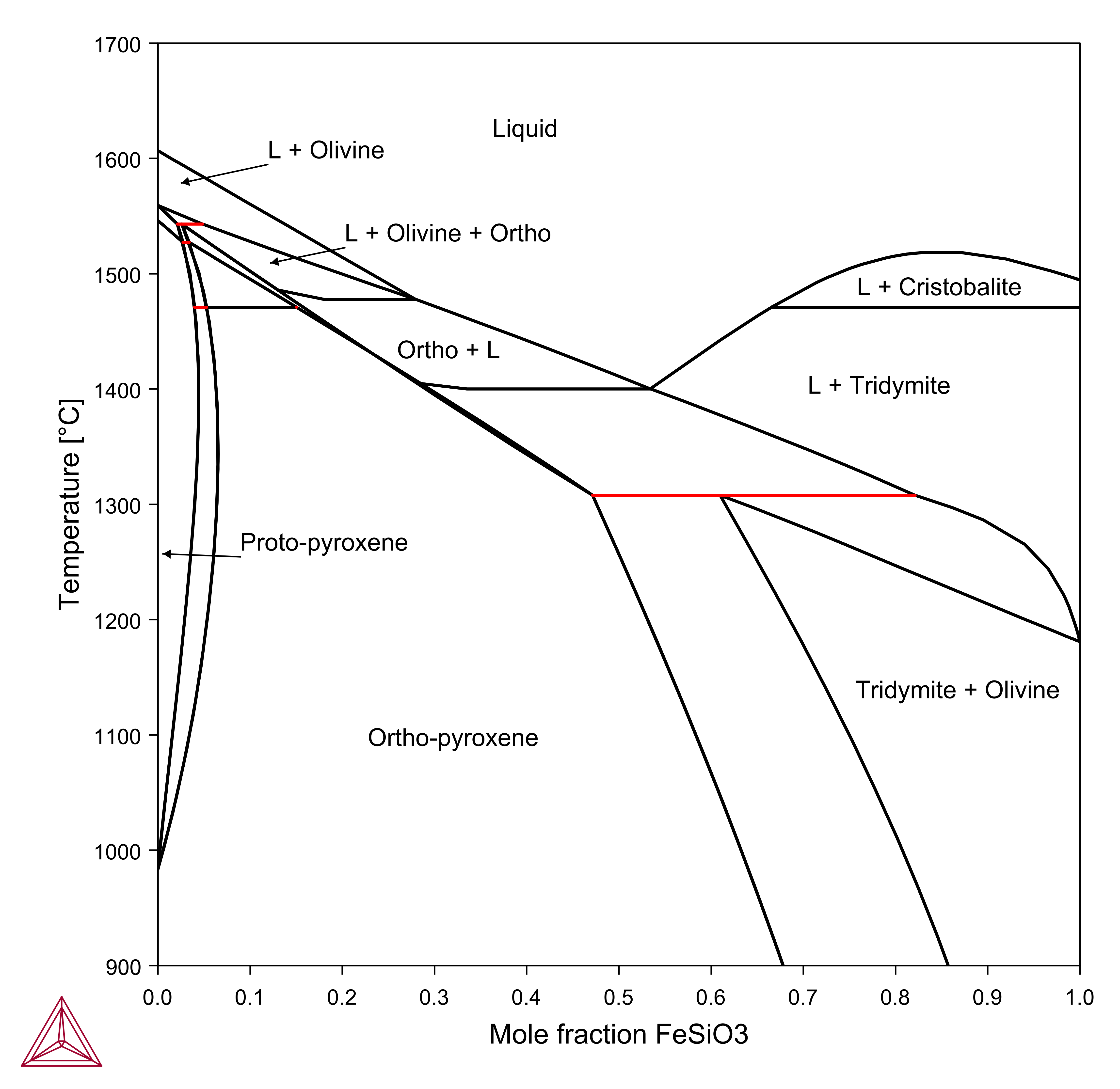
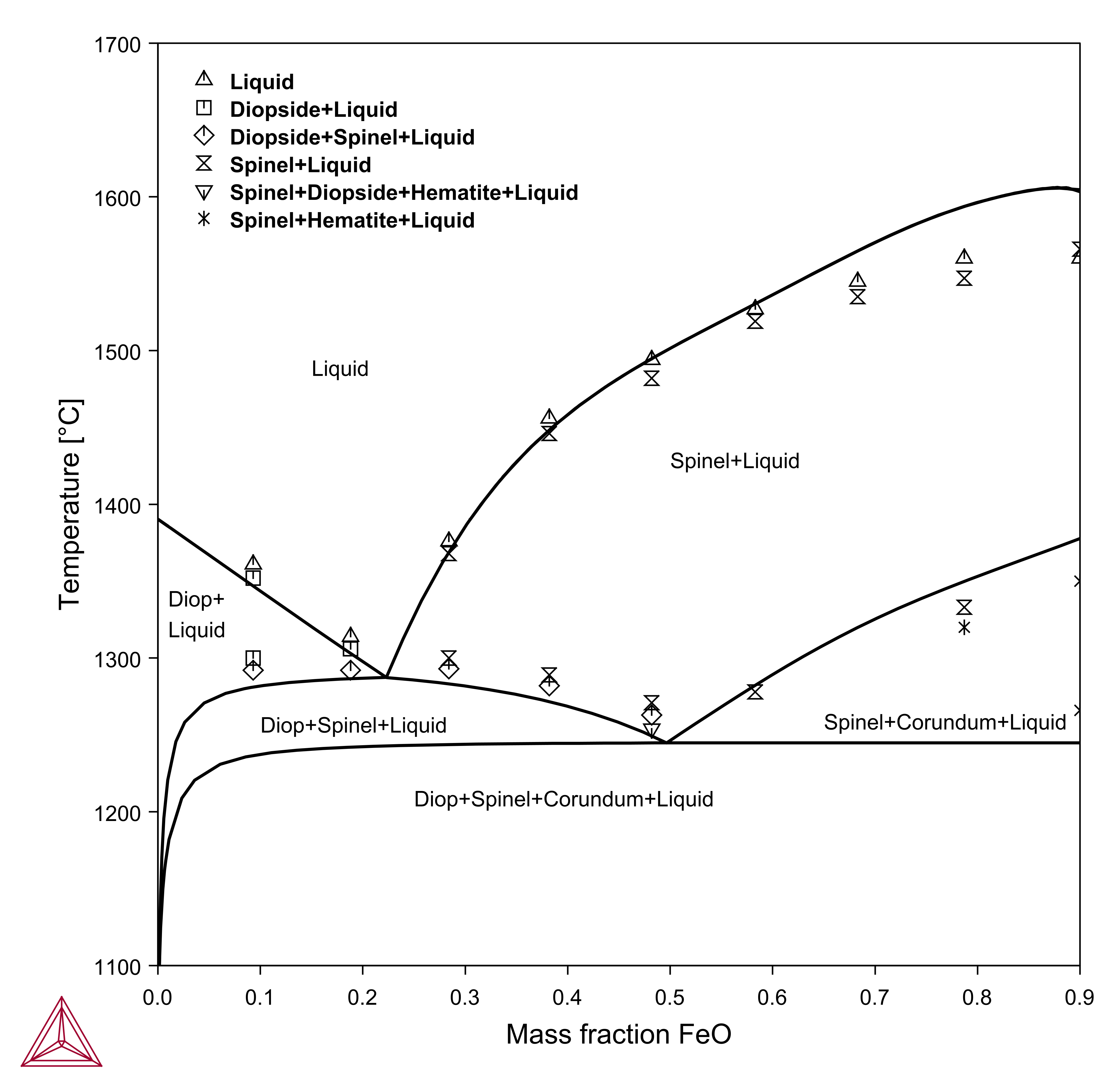
MgSiO3-FeSiO3
The MgSiO3-FeSiO3 section shown in this example is calculated using the components MGO, FEO, SIO2, O and the conditions AC(FE,FCC)=1, X(SIO2)=0.5.
Figure 1: Calculated "FeO"-MgO-SiO2 liquidus projection. Dashed curve is the pyroxene section MgSiO3-FeSiO3.
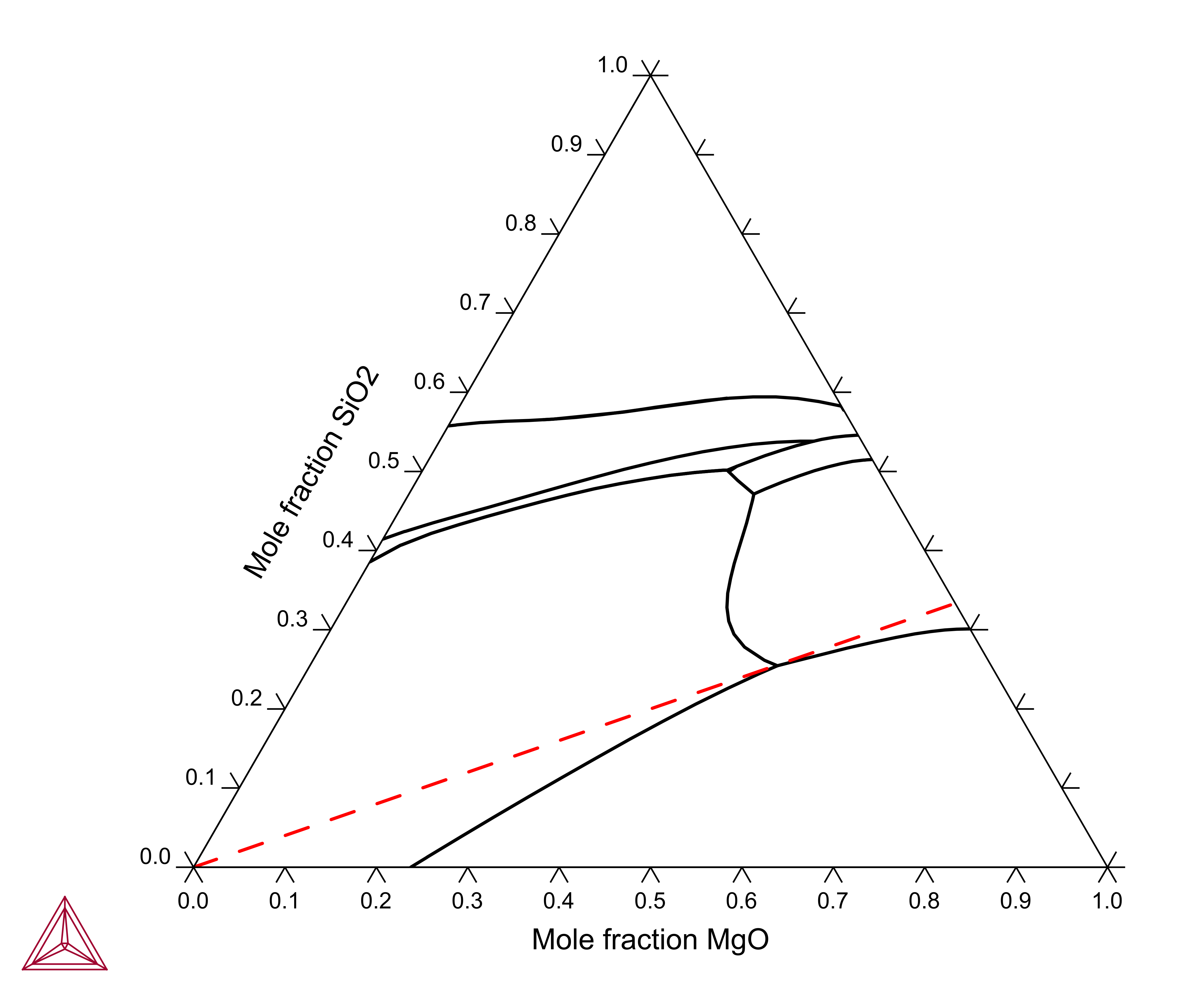
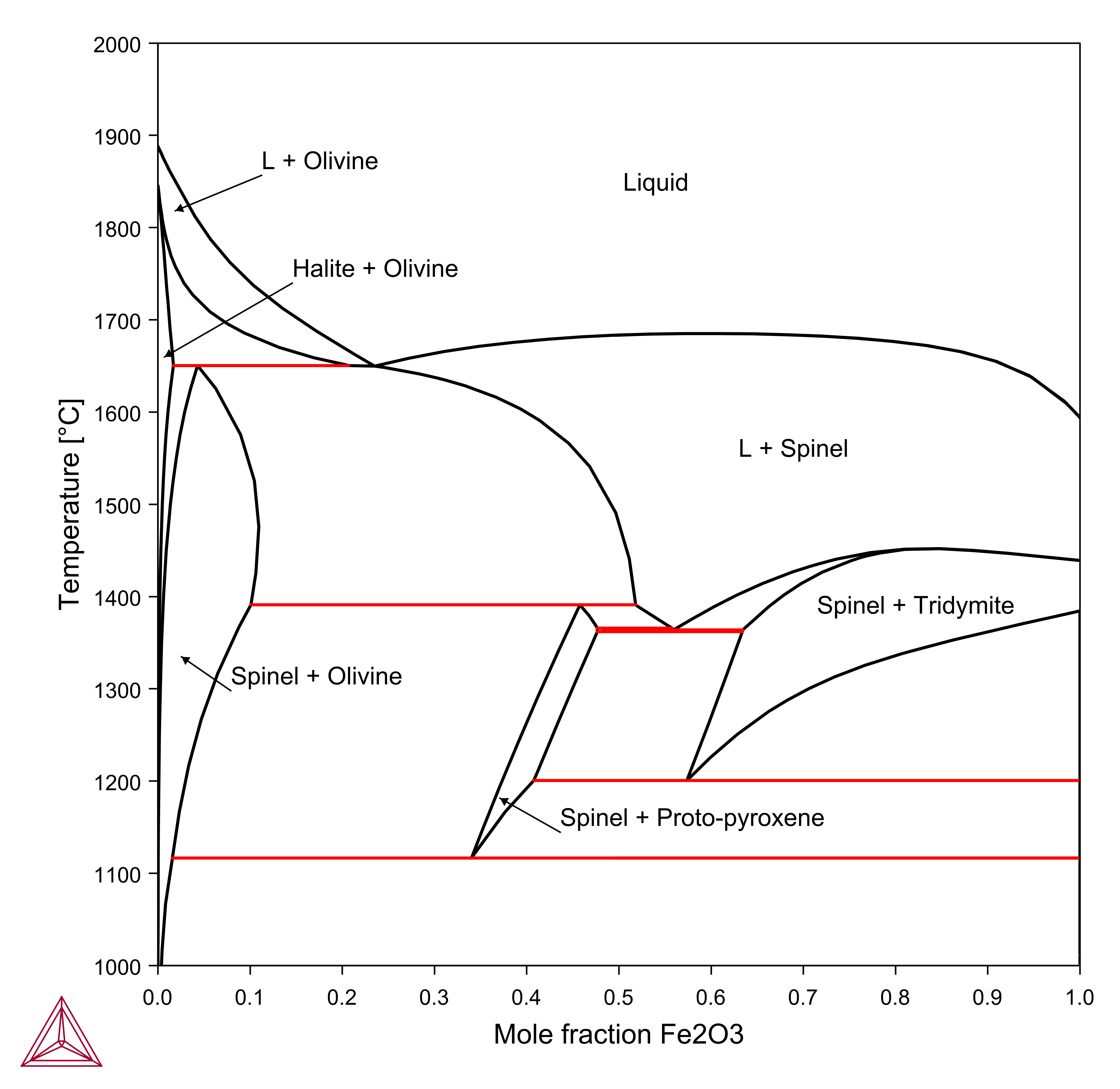
Fe2O3-Mg2SiO4
The Fe2O3-Mg2SiO4 section is calculated using the components MGO, FE2O3, SIO2, O. The section is calculated along a line where the MgO content is twice that of the SiO2 content, this can be used as a condition: AC(O2,GAS)=0.21, 2*X(SIO2)-X(MGO)=0.
Figure 3: Calculated "Fe2O3"-MgO-SiO2 liquidus projection. Dashed curve is the Fe2O3-Mg2SiO4 section.