Continuity Equation
Let 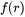 be the PSD of a precipitate phase,
be the PSD of a precipitate phase, 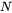 the number of particles per unit volume,
the number of particles per unit volume, 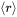 the mean radius and
the mean radius and 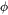 the particle volume fraction, is expressed as
the particle volume fraction, is expressed as
[Eq. 1]
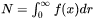
[Eq. 2]
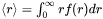
[Eq. 3]
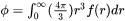
The time evolution of 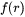 follows the continuity as in Langer and Schwartz [1980Lan].
follows the continuity as in Langer and Schwartz [1980Lan].
[Eq. 4]
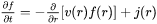
Where 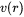 is the growth rate of a particle of size
is the growth rate of a particle of size  , and
, and 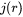 is the distributed nucleation rate, which is defined by
is the distributed nucleation rate, which is defined by
[Eq. 5]
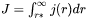
where 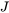 is the nucleation rate.
is the nucleation rate.
Reference
[1980Lan] J. S. Langer, A. J. Schwartz, Kinetics of nucleation in near-critical fluids. Phys. Rev. A. 21, 948–958 (1980).