Estimation of Coherent Interfacial Energy
Interfacial energy is an important parameter used in precipitation simulations to calculate the rates of nucleation, growth/dissolution, and coarsening. The value of interfacial energy can vary dramatically (usually between 0.01 to 2.0 J/m2).
The extended Becker’s model functions to estimate coherent interfacial energy by using thermodynamic data from existing CALPHAD thermodynamic databases:
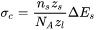
where 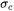 is the coherent interfacial energy,
is the coherent interfacial energy, 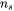 is the number of atoms per unit area at the interface,
is the number of atoms per unit area at the interface, 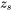 is the number of cross bonds per atom at the interface,
is the number of cross bonds per atom at the interface, 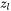 is the coordination number of an atom within the bulk crystal lattice, and
is the coordination number of an atom within the bulk crystal lattice, and 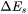 is the energy of solution in a multicomponent system involving the two phases being considered [1938Bec].
is the energy of solution in a multicomponent system involving the two phases being considered [1938Bec].
[1938Bec] R. Becker, Die Keimbildung bei der Ausscheidung in metallischen Mischkristallen. Ann. Phys. 424, 128–140 (1938).