T_19: Young's Modulus for Ti-O with Elastic Properties
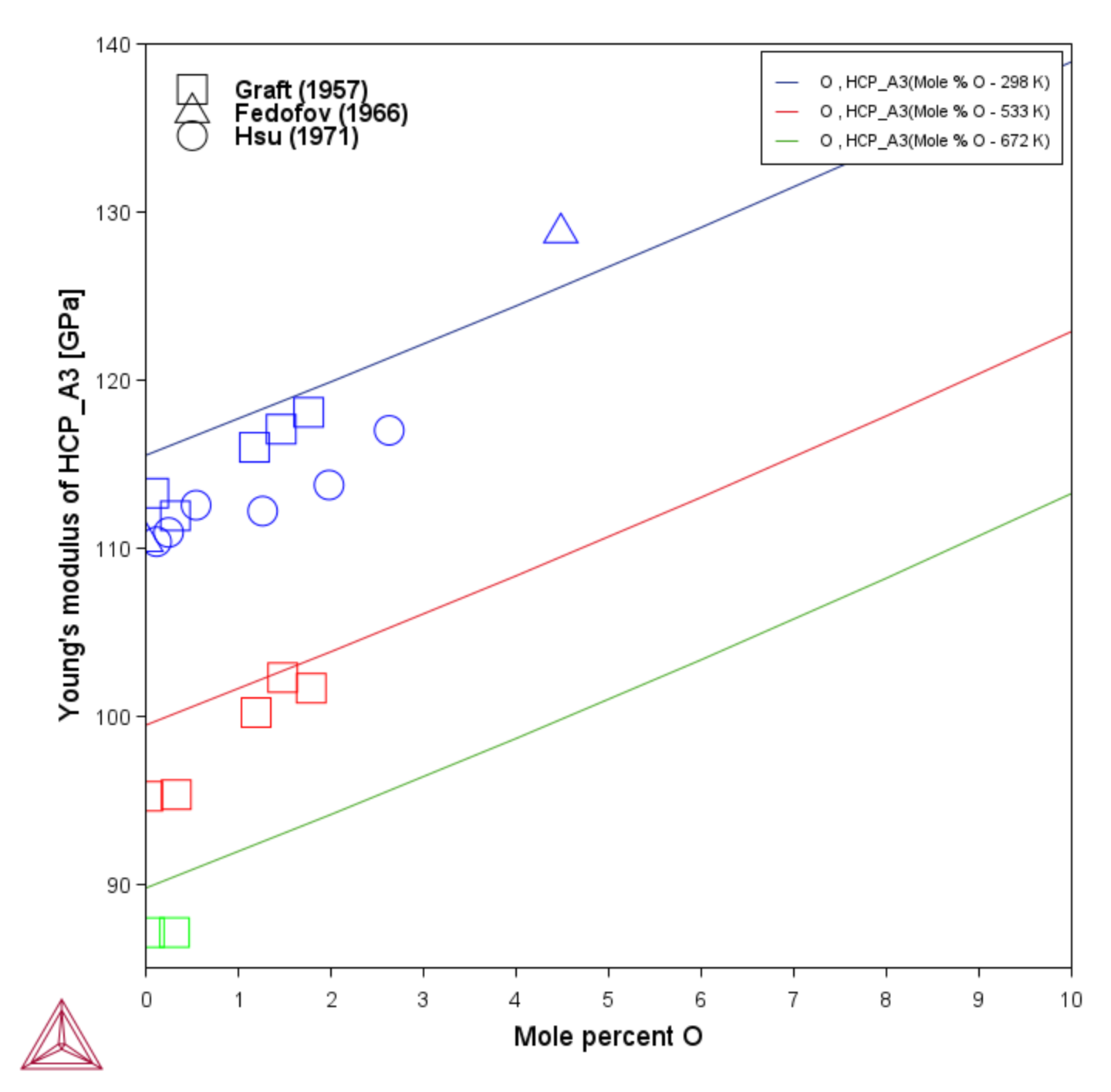
This is an example which shows the effect of oxygen concentration at three temperatures on an elastic property, Young's modulus, for the HCP_A3 phase in a Ti-O system.
It is well established in the literature that mechanical properties of titanium and its related alloys are sensitive to the presence of even dilute concentrations of interstitial solutes such as carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen and oxygen. It is therefore important to adequately model the effects of impurities in the host lattice when calculating mechanical properties, such as the elastic constants and the corresponding moduli determined from these constants.
Only the elastic constants are assessed, and then used to derive the elastic moduli, meaning the experimental data in the plot are completely standalone from the assessment process.
In this example, three Equilibrium Calculators are used with One Axis calculations at different temperatures (298 K, 533 K, and 672 K) to show the Young's modulus of an HCP_A3 phase as a function of mole percent of O and compared to experimental data from [1957Gra; 1966Fed; 1971Hsu].
- Folder: Thermo‑Calc
- File name: T_19_Elastic_Properties_YoungsModulus_Ti-O.tcu
The TCS Ti/TiAl-based Alloys Database (TCTI) is used in this example. A valid license is required to run the example.
Visualizations
Many of our Graphical Mode examples have video tutorials, which you can access in a variety of ways. When in Thermo‑Calc, from the menu select Help → Video Tutorials, or from the main My Project window, click Video Tutorials. Alternately, you can go to the website or our YouTube channel.
Open the example project file to review the node setup on the Project window and the associated settings on the Configuration window for each node. For some types of projects, you can also adjust settings on the Plot Renderer Configuration window to preview results before performing the simulation. Click Perform Tree to generate plots and tables to see the results on the Visualizations window.
Figure 1: Effect of oxygen on Young’s modulus in HCP_A3 titanium compared to experimental data [1957Gra; 1966Fed; 1971Hsu].
References
[1957Gra] W. H. Graft, D. W. Levinson and W. Rostoker, The influence of alloying on the elastic modulus of titanium alloys, Trans. Am. Soc. Met. 49, 263-279 (1957).
[1966Fed] S. G. Fedofov, Titanium and Its Alloys, Publ. No. lO, I. I. Kornilov Editor, Israel Prog. Sci. Trans., 199 (1966).
[1971Hsu] N. Hsu, H. Conrad, Ultrasonic wave velocity measurements on titanium-oxygen alloys. Scr. Metall. 5, 905–908 (1971).
More Information
As of Thermo-Calc version 2025b, elastic properties are available with Thermo‑Calc and the TCS Ti/TiAl-based Alloys Database (TCTI) (TCTI6 and newer), TCS Steel and Fe-alloys Database (TCFE) (TCFE14 and newer), TCS High Entropy Alloys Database (TCHEA) (TCHEA8 and newer), and TCS Ni-based Superalloys Database (TCNI) (TCNI13 and newer). These elastic properties will be added to additional databases over time. Subscribe to our newsletter to be kept up-to-date on the latest product releases, webinars, user group meetings, applications examples, and more.
For more information about the theory about the elastic properties, which includes constants and moduli, see About the Elastic Properties.